Blockade of costimulation prevents infection-induced immunopathology in interleukin-10-deficient mice
- PMID: 10768980
- PMCID: PMC97495
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.68.5.2837-2844.2000
Blockade of costimulation prevents infection-induced immunopathology in interleukin-10-deficient mice
Abstract
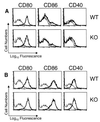
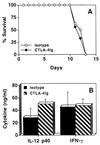
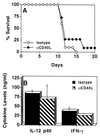
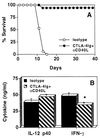
Interleukin-10 (IL-10) is associated with inhibition of cell-mediated immunity and downregulation of the expression of costimulatory molecules required for T-cell activation. When IL-10-deficient (IL-10KO) mice are infected with Toxoplasma gondii, they succumb to a T-cell-mediated shock-like reaction characterized by the overproduction of IL-12 and gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) associated with widespread necrosis of the liver. Since costimulation is critical for T-cell activation, we investigated the role of the CD28-B7 and CD40-CD40 ligand (CD40L) interactions in this infection-induced immunopathology. Our studies show that infection of mice with T. gondii resulted in increased expression of B7 and CD40 that was similar in wild-type and IL-10KO mice. In vivo blockade of the CD28-B7 or CD40-CD40L interactions following infection of IL-10KO mice with T. gondii did not affect serum levels of IFN-gamma or IL-12, nor did it prevent death in these mice. However, when both pathways were blocked, the IL-10KO mice survived the acute phase of infection and had reduced serum levels of IFN-gamma and alanine transaminase as well as decreased expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in the liver and spleen. Analysis of parasite-specific recall responses from infected IL-10KO mice revealed that blockade of the CD40-CD40L interaction had minimal effects on cytokine production, whereas blockade of the CD28-B7 interaction resulted in decreased production of IFN-gamma but not IL-12. Further reduction of IFN-gamma production was observed when both costimulatory pathways were blocked. Together, these results demonstrate that the CD28-B7 and CD40-CD40L interactions are involved in the development of infection-induced immunopathology in the absence of IL-10.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Contribution of interleukin-12 (IL-12) and the CD28/B7 and CD40/CD40 ligand pathways to the development of a pathological T-cell response in IL-10-deficient mice.Infect Immun. 2002 Dec;70(12):6940-7. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.12.6940-6947.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 12438373 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of CD28-B7, but not CD40-CD154, prevents costimulation of allogeneic porcine and xenogeneic human anti-porcine T cell responses.J Immunol. 2000 Mar 15;164(6):3434-44. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.6.3434. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10706740
-
Aggressive skin allograft rejection in CD28-/- mice independent of the CD40/CD40L costimulatory pathway.Transpl Immunol. 2001 Oct;9(1):13-7. doi: 10.1016/s0966-3274(01)00043-0. Transpl Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11680567
-
Role of B7 signaling in the differentiation of naive CD4+ T cells to effector interleukin-4-producing T helper cells.Immunol Res. 1995;14(3):176-88. doi: 10.1007/BF02918215. Immunol Res. 1995. PMID: 8778208 Review.
-
Targeting T cell costimulation in autoimmune disease.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2002 Jun;6(3):275-89. doi: 10.1517/14728222.6.3.275. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2002. PMID: 12223069 Review.
Cited by
-
Diverse roles for T-bet in the effector responses required for resistance to infection.J Immunol. 2015 Feb 1;194(3):1131-40. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401617. Epub 2015 Jan 2. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25556247 Free PMC article.
-
Ups and downs of mucosal cellular immunity against protozoan parasites.Infect Immun. 2001 Jan;69(1):1-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.1.1-8.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11119482 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Conventional T-bet(+)Foxp3(-) Th1 cells are the major source of host-protective regulatory IL-10 during intracellular protozoan infection.J Exp Med. 2007 Feb 19;204(2):273-83. doi: 10.1084/jem.20062175. Epub 2007 Feb 5. J Exp Med. 2007. PMID: 17283209 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of interleukin-12 (IL-12) and the CD28/B7 and CD40/CD40 ligand pathways to the development of a pathological T-cell response in IL-10-deficient mice.Infect Immun. 2002 Dec;70(12):6940-7. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.12.6940-6947.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 12438373 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of Interleukin-10 (IL-10) Signaling Promotes IL-22-Dependent Host Defenses against Acute Clostridioides difficile Infection.Infect Immun. 2021 Apr 16;89(5):e00730-20. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00730-20. Print 2021 Apr 16. Infect Immun. 2021. PMID: 33649048 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blewett D A, Miller J K, Harding J. Simple technique for the direct isolation of toxoplasma tissue cysts from fetal ovine brains. Vet Rec. 1983;112:98–100. - PubMed
-
- Brinkmann V, Sharma S D, Remington J S. Differential regulation of the L3T4-T cell subset by B-cells in different mouse strains bearing the H-2k haplotype. J Immunol. 1986;137:2991–2997. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

