Image registration using a symmetric prior--in three dimensions
- PMID: 10770230
- PMCID: PMC6871943
- DOI: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0193(200004)9:4<212::aid-hbm3>3.0.co;2-#
Image registration using a symmetric prior--in three dimensions
Abstract
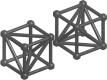
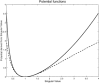
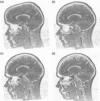
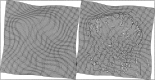
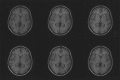
This paper describes a Bayesian method for three-dimensional registration of brain images. A finite element approach is used to obtain a maximum a posteriori estimate of the deformation field at every voxel of a template volume. The priors used by the MAP estimate penalize unlikely deformations and enforce a continuous one-to-one mapping. The deformations are assumed to have some form of symmetry, in that priors describing the probability distribution of the deformations should be identical to those for the inverses (i.e., warping brain A to brain B should not be different probablistically from warping B to A). A gradient descent algorithm is presented for estimating the optimum deformations.
Figures

References
-
- Amit Y, Grenander U, Piccioni M. 1991: Structural image restoration through deformable templates. J Am Stat Assoc 86: 376–387.
-
- Ashburner J, Friston KJ. 1997: Multimodal image coregistration and partitioning—a unified framework. NeuroImage 6: 209–217. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J, Neelin P, Collins DL, Evans AC, Friston KJ. 1997: Incorporating prior knowledge into image registration. NeuroImage 6: 344–352. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J, Andersson J, Friston KJ. 1999: High‐dimensional nonlinear image registration using symmetric priors. NeuroImage 9: 619–628. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

