In vitro pharmacodynamic parameters of sordarin derivatives in comparison with those of marketed compounds against Pneumocystis carinii isolated from rats
- PMID: 10770763
- PMCID: PMC89856
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.44.5.1284-1290.2000
In vitro pharmacodynamic parameters of sordarin derivatives in comparison with those of marketed compounds against Pneumocystis carinii isolated from rats
Abstract
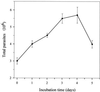
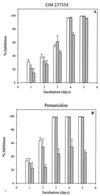
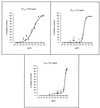
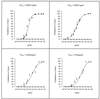
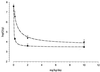
Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia remains one of the most serious complications of immunosuppressed patients. In this study, the in vitro pharmacodynamic parameters of four sordarin derivatives (GM 191519, GM 237354, GM 193663, and GM 219771) have been evaluated by a new quantitative approach and compared with the commercially available drugs pentamidine, atovaquone, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX). In vitro activities and in vivo therapeutic efficacies of sordarin derivatives against P. carinii were also evaluated. In vitro activity was determined by the broth microdilution technique, comparing the total number of microorganisms in treated and drug-free cultures by using Giemsa staining. The in vitro maximum effect (E(max)), the drug concentrations to reach 50% of E(max) (EC(50)), and the slope of the dose-response curve were then estimated by the Hill equation (E(max) sigmoid model). Sordarin derivatives were the most potent agents against P. carinii, with EC(50)s of 0.00025, 0.0007, 0.0043, and 0. 025 microg/ml for GM 191519, GM 237354, GM 193663, and GM 219771, respectively. The EC(50)s of pentamidine, atovaquone, and TMP-SMX were 0.025, 0.16, and 26.7/133.5 microg/ml, respectively. The results obtained with this approach showed GM 237354 and GM 191519 to be approximately 35- and 100-fold more active in vitro than pentamidine, the most active marketed compound. All sordarin derivatives tested were at least 5,000-fold more active in vitro than TMP-SMX. The three sordarin derivatives tested in vivo-GM 191519, GM 237354, and GM 219771-showed a marked therapeutic efficacy, defined as reduction of cyst forms per gram of lung. GM 191519 was the most potent (daily dose reducing 50% of the P. carinii burden in the lungs [ED(50)], 0.05 mg/kg/day) followed by GM 237354 and GM 219771 (ED(50)s, 0.30 and 0.49 mg/kg/day, respectively). Good agreement between in vitro parameters and in vivo outcome was obtained when P. carinii pneumonia in rats was treated with sordarin derivatives.
Figures

References
-
- Acred P, Hennessey T D, MacArthur-Clark J A, Merrikin D J, Ryan D M, Smulders H C, Troke P F, Wilson R G, Straughan D W. Guidelines for the welfare of animals in rodent protection tests. A report from the rodent test working party. Lab Anim. 1994;28:13–18. - PubMed
-
- Aliouat E M, Martinez A, Jimenez E, Dei-Cas E, Mullet C, Delcourt P, Gargallo-Viola D. Development of Pneumocystis animal models: corticosteroid-treated Wistar rat; SCID mouse and Nude rat. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 1997;44:41S–42S. - PubMed
-
- Aliouat E M, Dei-Cas E, Ouassi M A, Palluault F, Soulez B, Camus D. In vitro attachment of Pneumocystis carinii from mouse and rat origin. Biol Cell. 1993;77:209–217. - PubMed
-
- Aliouat E M, Mazars E, Dei-Cas E, Cesbron J Y, Camus D. Intranasal inoculation of mouse, rat or rabbit-derived Pneumocystis in SCID mouse. J Protozool Res. 1993;3:94–98.
-
- Aliouat E M, Dujardin L, Martinez A, Duriez T, Dei-Cas E. Pneumocystis carinii growth kinetics in culture systems and in hosts: involvement of each life cycle parasite stage. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 1999;46:116S–117S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

