Continuous low-dose therapy with vinblastine and VEGF receptor-2 antibody induces sustained tumor regression without overt toxicity
- PMID: 10772661
- PMCID: PMC517491
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI8829
Continuous low-dose therapy with vinblastine and VEGF receptor-2 antibody induces sustained tumor regression without overt toxicity
Erratum in
- J Clin Invest. 2006 Nov;116(11):3084
- J Clin Invest. 2006 Oct;116(10):2827
Abstract
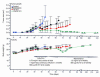
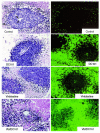
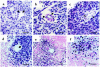
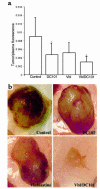
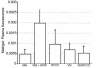
Various conventional chemotherapeutic drugs can block angiogenesis or even kill activated, dividing endothelial cells. Such effects may contribute to the antitumor efficacy of chemotherapy in vivo and may delay or prevent the acquisition of drug-resistance by cancer cells. We have implemented a treatment regimen that augments the potential antivascular effects of chemotherapy, that is devoid of obvious toxic side effects, and that obstructs the development of drug resistance by tumor cells. Xenografts of 2 independent neuroblastoma cell lines were subjected to either continuous treatment with low doses of vinblastine, a monoclonal neutralizing antibody (DC101) targeting the flk-1/KDR (type 2) receptor for VEGF, or both agents together. The rationale for this combination was that any antivascular effects of the low-dose chemotherapy would be selectively enhanced in cells of newly formed vessels when survival signals mediated by VEGF are blocked. Both DC101 and low-dose vinblastine treatment individually resulted in significant but transient xenograft regression, diminished tumor vascularity, and direct inhibition of angiogenesis. Remarkably, the combination therapy resulted in full and sustained regressions of large established tumors, without an ensuing increase in host toxicity or any signs of acquired drug resistance during the course of treatment, which lasted for >6 months. This article may have been published online in advance of the print edition. The date of publication is available from the JCI website, http://www.jci.org.
Figures
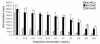
Comment in
-
Less is more, regularly: metronomic dosing of cytotoxic drugs can target tumor angiogenesis in mice.J Clin Invest. 2000 Apr;105(8):1045-7. doi: 10.1172/JCI9872. J Clin Invest. 2000. PMID: 10772648 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kerbel RS. Tumor angiogenesis: past, present, and the near future. Carcinogenesis. 2000;21:505–515. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N, Alitalo K. Clinical applications of angiogenic growth factors and their inhibitors. Nat Med. 1999;5:1359–1364. - PubMed
-
- Presta LG, et al. Humanization of an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor monoclonal antibody for the therapy of solid tumors and other disorders. Cancer Res. 1997;57:4593–4599. - PubMed
-
- Witte L, et al. Monoclonal antibodies targeting the VEGF receptor-2 (Flk1/KDR) as an anti-angiogenic therapeutic strategy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1998;17:155–161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

