Structural organization of Staf-DNA complexes
- PMID: 10773080
- PMCID: PMC105361
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/28.10.2114
Structural organization of Staf-DNA complexes
Abstract
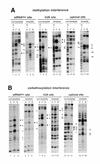
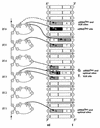
The transactivator Staf, which contains seven contiguous zinc fingers of the C(2)-H(2)type, exerts its effects on gene expression by binding to specific targets in vertebrate small nuclear RNA (snRNA) and snRNA-type gene promoters. Here, we have investigated the interaction of the Staf zinc finger domain with the optimal Xenopus selenocysteine tRNA (xtRNA(Sec)) and human U6 snRNA (hU6) Staf motifs. Generation of a series of polypeptides containing increasing numbers of Staf zinc fingers tested in binding assays, by interference techniques and by binding site selection served to elucidate the mode of interaction between the zinc fingers and the Staf motifs. Our results provide strong evidence that zinc fingers 3-6 represent the minimal zinc finger region for high affinity binding to Staf motifs. Furthermore, we show that the binding of Staf is achieved through a broad spectrum of close contacts between zinc fingers 1-6 and xtRNA(Sec)or optimal sites or between zinc fingers 3-6 and the hU6 site. Extensive DNA major groove contacts contribute to the interaction with Staf that associates more closely with the non-template than with the template strand. Based on these findings and the structural information provided by the solved structures of other zinc finger-DNA complexes, we propose a model for the interaction between Staf zinc fingers and the xtRNA(Sec), optimal and hU6 sites.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Maximization of selenocysteine tRNA and U6 small nuclear RNA transcriptional activation achieved by flexible utilization of a Staf zinc finger.J Biol Chem. 1999 Aug 27;274(35):25042-50. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.35.25042. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10455183
-
Flexible zinc finger requirement for binding of the transcriptional activator staf to U6 small nuclear RNA and tRNA(Sec) promoters.J Biol Chem. 1999 Aug 20;274(34):24241-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.34.24241. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10446199
-
Staf, a promiscuous activator for enhanced transcription by RNA polymerases II and III.EMBO J. 1997 Jan 2;16(1):173-81. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.1.173. EMBO J. 1997. PMID: 9009278 Free PMC article.
-
Staf, a novel zinc finger protein that activates the RNA polymerase III promoter of the selenocysteine tRNA gene.EMBO J. 1995 Aug 1;14(15):3777-87. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00047.x. EMBO J. 1995. PMID: 7641696 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple modes of RNA recognition by zinc finger proteins.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2005 Jun;15(3):367-73. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2005.04.004. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2005. PMID: 15963892 Review.
Cited by
-
ZNF143 protein is an important regulator of the myeloid transcription factor C/EBPα.J Biol Chem. 2017 Nov 17;292(46):18924-18936. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.811109. Epub 2017 Sep 12. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28900037 Free PMC article.
-
Forced Expression of ZNF143 Restrains Cancer Cell Growth.Cancers (Basel). 2011 Oct 19;3(4):3909-20. doi: 10.3390/cancers3043909. Cancers (Basel). 2011. PMID: 24213117 Free PMC article.
-
RNA Polymerase III Subunit Mutations in Genetic Diseases.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Jul 30;8:696438. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.696438. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34395528 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CTCF As an Example of DNA-Binding Transcription Factors Containing Clusters of C2H2-Type Zinc Fingers.Acta Naturae. 2021 Jan-Mar;13(1):31-46. doi: 10.32607/actanaturae.11206. Acta Naturae. 2021. PMID: 33959385 Free PMC article.
-
Bidirectional activity of the NWC promoter is responsible for RAG-2 transcription in non-lymphoid cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44807. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044807. Epub 2012 Sep 11. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22984564 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rosenberg U.B., Schröder,C., Preiss,A., Kienlin,A., Cote,S., Riede,I. and Jäckle,H. (1986) Nature, 319, 336–339.
-
- Tautz D., Lehmann,R., Schnürch,H., Schuh,R., Seifert,E., Kienlin,A., Jones,K. and Jäckle,H. (1987) Nature, 327, 383–389.
-
- Turner J. and Crossley,M. (1999) Trends Biochem. Sci., 24, 236–240. - PubMed
-
- Schuh R., Aicher,W., Gaul,U., Côté,S., Preiss,A., Maier,D., Seifert,E., Nauber,U., Schröder,C., Kemler,R. and Jäckle,H. (1986) Cell, 47, 1025–1032. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

