Interleukin-10 increases Th1 cytokine production and cytotoxic potential in human papillomavirus-specific CD8(+) cytotoxic T lymphocytes
- PMID: 10775611
- PMCID: PMC111995
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.10.4729-4737.2000
Interleukin-10 increases Th1 cytokine production and cytotoxic potential in human papillomavirus-specific CD8(+) cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Abstract
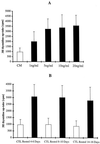
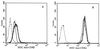
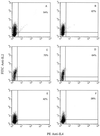
Interleukin-10 (IL-10) is widely known as an immunosuppressive cytokine by virtue of its ability to inhibit macrophage-dependent antigen presentation, T-cell proliferation, and Th1 cytokine secretion. However, several studies have challenged the perception of IL-10 solely as an immunosuppressive cytokine. As part of an investigation on potentiation of the cytotoxic activity of human papillomavirus E7-specific CD8(+) cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) for adoptive transfusions to cervical cancer patients, we found that IL-10 in combination with IL-2, unlike several other combinations, including IL-2 with IL-12, gamma interferon (IFN-gamma), tumor necrosis factor alpha, and transforming growth factor beta, was able to consistently increase cytotoxicity. This augmentation in cytotoxic activity correlated with a significant increase in the cytoplasmic accumulation of perforin as detected by fluorescence-activated cell sorter. Surface expression of both the alpha and beta chains of the CD8 heterodimeric coreceptor and CD56 molecules was increased by exposure of CTL to IL-10. More importantly, we found that administration of IL-10 in combination with IL-2 after antigen stimulation consistently increased the intracellular expression of Th1 cytokines (i.e., IFN-gamma and IL-2) compared to results for control CD8(+) T cells cultured in IL-2 alone. In kinetic studies, proliferation, intracellular perforin levels, cytotoxic activity, and IFN-gamma expression were consistently elevated in CTL cultures containing IL-10 compared to control cultures, both at early and late time points following stimulation. In contrast, intracellular IL-2 expression was consistently increased only at early time points following stimulation with autologous tumor cells or solid-phase anti-CD3 antibody. Taken together, these data support the use of IL-10 in combination with IL-2 for the in vitro expansion and potentiation of tumor-specific CTL for clinical use in the therapy of cancer.
Figures


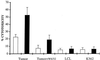


Similar articles
-
Expression of CD56 by human papillomavirus E7-specific CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes correlates with increased intracellular perforin expression and enhanced cytotoxicity against HLA-A2-matched cervical tumor cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2001 Mar;7(3 Suppl):804s-810s. Clin Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11300476
-
Effect of blood transfusion during radiotherapy on the immune function of patients with cancer of the uterine cervix: role of interleukin-10.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002 Dec 1;54(5):1345-55. doi: 10.1016/s0360-3016(02)03757-4. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002. PMID: 12459356
-
Induction of tumor-specific cytotoxicity in tumor infiltrating lymphocytes by HPV16 and HPV18 E7-pulsed autologous dendritic cells in patients with cancer of the uterine cervix.Gynecol Oncol. 2003 May;89(2):271-80. doi: 10.1016/s0090-8258(03)00083-0. Gynecol Oncol. 2003. PMID: 12713991 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of asbestos exposure on differentiation and function of cytotoxic T lymphocytes.Environ Health Prev Med. 2020 Oct 8;25(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12199-020-00900-6. Environ Health Prev Med. 2020. PMID: 33032525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The defect of the perforin granule system in cytotoxic T lymphocytes of atopic patients--are perforin reduction and hyperreleasability of clinical relevance?J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2003 Dec;1(12):938-44. doi: 10.1046/j.1439-0353.2003.03018.x. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2003. PMID: 16285645 Review.
Cited by
-
IL-10 signaling in CD4+ T cells is critical for the pathogenesis of collagen-induced arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(6):R212. doi: 10.1186/ar3545. Epub 2011 Dec 22. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011. PMID: 22192790 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-10 and pathogenesis of murine ocular toxoplasmosis.Infect Immun. 2003 Dec;71(12):7159-63. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.12.7159-7163.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 14638808 Free PMC article.
-
TIMP-1-GPI in combination with hyperthermic treatment of melanoma increases sensitivity to FAS-mediated apoptosis.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2009 Mar;58(3):361-71. doi: 10.1007/s00262-008-0559-5. Epub 2008 Jul 11. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2009. PMID: 18618109 Free PMC article.
-
Current status of interleukin-10 and regulatory T-cells in cancer.Curr Opin Oncol. 2013 Nov;25(6):637-45. doi: 10.1097/CCO.0000000000000006. Curr Opin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24076584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-10-induced gp130 expression in mouse mast cells permits IL-6 trans-signaling.J Leukoc Biol. 2012 Mar;91(3):427-35. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0411209. Epub 2011 Dec 2. J Leukoc Biol. 2012. PMID: 22140267 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baxevanis C N, Papamichail M. Characterization of an anti-tumor immune response in human cancers and strategies for immunotherapy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 1994;16:157–179. - PubMed
-
- Berman R M, Suzuki T, Tahara H, Robbins P D, Narula S, Lotze M T. Systemic administration of cellular interleukin-10 induces an effective, specific, and long lived immune response against established tumors in mice. J Immunol. 1996;157:231–237. - PubMed
-
- Blazar B R, Taylor P A, Smith S, Vallera D A. Interleukin-10 administration decreases survival in murine recipients of major histocompatibility complex disparate donor bone marrow grafts. Blood. 1995;85:842–850. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

