Involvement of retinoblastoma family members and E2F/DP complexes in the death of neurons evoked by DNA damage
- PMID: 10777774
- PMCID: PMC6773109
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-09-03104.2000
Involvement of retinoblastoma family members and E2F/DP complexes in the death of neurons evoked by DNA damage
Abstract
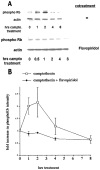
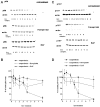
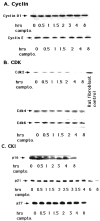
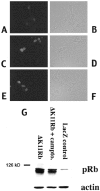
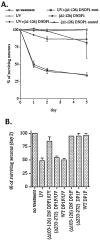
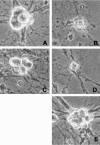
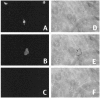
Neuronal death evoked by DNA damage requires cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (Cdk4) and 6 activity and is accompanied by elevation of cyclin D1-associated kinase activity. Because Cdk4/6 phosphorylates retinoblastoma protein (pRb) family members that then modulate the transcriptional activity of E2F/DP1 complexes, we examined the involvement of these components in DNA damage-evoked neuronal death. Camptothecin induced rapid pRb and p107 phosphorylation at a Cdk4/6 phosphorylation site followed by selective loss of Rb and p107. The CDK inhibitor flavopiridol suppressed pRb and p107 phosphorylation and loss, implicating CDK activity in these events. Moreover, the loss of pRb and p107 appeared to be mediated by caspases because it was blocked by general caspase inhibitors. The role of phosphorylation and pRb and p107 loss in the death pathway was indicated by observations that virally mediated expression of pRb mutated at sites of phosphorylation, including the Cdk4/6 site, inhibited death. Finally, expression of dominant-negative versions of DP1, known to compromise E2F transcriptional activity, protects cortical neurons from death induced by camptothecin and sympathetic neurons from death evoked by UV treatment. Taken together, these results implicate the CDK-pRb/E2F/DP pathway as a required element in the neuronal death evoked by DNA damage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression and activity of the retinoblastoma protein (pRB)-family proteins, p107 and p130, during L6 myoblast differentiation.Cell Growth Differ. 1995 Oct;6(10):1287-98. Cell Growth Differ. 1995. PMID: 8845306
-
The interactions of E2F with pRB and with p107 are regulated via the phosphorylation of pRB and p107 by a cyclin-dependent kinase.Oncogene. 1995 May 4;10(9):1691-8. Oncogene. 1995. PMID: 7753545
-
Involvement of cell cycle elements, cyclin-dependent kinases, pRb, and E2F x DP, in B-amyloid-induced neuronal death.J Biol Chem. 1999 Jul 2;274(27):19011-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.27.19011. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10383401
-
[Molecular mechanisms controlling the cell cycle: fundamental aspects and implications for oncology].Cancer Radiother. 2001 Apr;5(2):109-29. doi: 10.1016/s1278-3218(01)00087-7. Cancer Radiother. 2001. PMID: 11355576 Review. French.
-
Activity of the retinoblastoma family proteins, pRB, p107, and p130, during cellular proliferation and differentiation.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1996 Jun;31(3):237-71. doi: 10.3109/10409239609106585. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1996. PMID: 8817077 Review.
Cited by
-
A reevaluation of tetraploidy in the Alzheimer's disease brain.Neurodegener Dis. 2009;6(5-6):221-9. doi: 10.1159/000236901. Epub 2009 Sep 9. Neurodegener Dis. 2009. PMID: 19738367 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase activity is required for apoptotic death but not inclusion formation in cortical neurons after proteasomal inhibition.J Neurosci. 2003 Feb 15;23(4):1237-45. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-04-01237.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12598612 Free PMC article.
-
Cell cycle activation and spinal cord injury.Neurotherapeutics. 2011 Apr;8(2):221-8. doi: 10.1007/s13311-011-0028-2. Neurotherapeutics. 2011. PMID: 21373950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aberrant activation of neuronal cell cycle caused by dysregulation of ubiquitin ligase Itch results in neurodegeneration.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Jun 8;11(6):441. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2647-1. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32513985 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal injury external to the retina rapidly activates retinal glia, followed by elevation of markers for cell cycle re-entry and death in retinal ganglion cells.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 1;9(7):e101349. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101349. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24983470 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beijersbergen RL, Carlee L, Kerkhoven RM, Bernards R. Regulation of the retinoblastoma protein-related p107 by G1 cyclin complexes. Genes Dev. 1995;9:1340–1350. - PubMed
-
- Berry DE, Lu Y, Schimdt B, Falon PG, O'Connell C, Hu S-X, Xu H-J, Blanck G. Retinoblastoma protein inhibits IFN induced apoptosis. Oncogene. 1996;12:1809–1819. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
