Reluctant gating of single N-type calcium channels during neurotransmitter-induced inhibition in bullfrog sympathetic neurons
- PMID: 10777775
- PMCID: PMC6773141
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-09-03115.2000
Reluctant gating of single N-type calcium channels during neurotransmitter-induced inhibition in bullfrog sympathetic neurons
Abstract
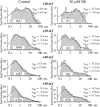
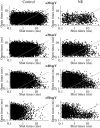
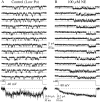
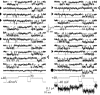
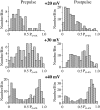
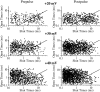
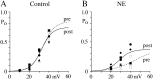
Whole-cell recordings have been used to extensively characterize the voltage-dependent inhibition of N-type calcium current induced by various neurotransmitters. Results from these studies have yielded several predictions on the effect of inhibition on N-channel gating, namely delayed channel opening and inhibition-induced reluctant openings. Previous single N-channel studies observed delayed channel opening but failed to find reluctant openings. However, strong depolarizations may be necessary to see reluctant openings, but this was not tested. We have examined N-channel gating at voltages depolarized to those used previously and found a neurotransmitter-induced open state that has properties predicted for the reluctant open state. The openings had lower open probability (P(o)) and brief open times compared to the dominant gating state observed in control (high P(o)). These reluctant events were reduced after strong depolarizing pulses used to reverse inhibition. The threshold voltage for activation of reluctant events was approximately 30 mV depolarized to that of the normal gating state (high P(o)). However, an action potential will provide sufficient depolarization to open reluctant N-channels.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Multiple modes of N-type calcium channel activity distinguished by differences in gating kinetics.J Neurosci. 1993 Jan;13(1):181-94. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-01-00181.1993. J Neurosci. 1993. PMID: 8380849 Free PMC article.
-
G-protein inhibition of N- and P/Q-type calcium channels: distinctive elementary mechanisms and their functional impact.J Neurosci. 2001 Feb 15;21(4):1137-47. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-04-01137.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11160384 Free PMC article.
-
Gating of single N-type calcium channels recorded from bullfrog sympathetic neurons.J Gen Physiol. 1999 Jan;113(1):111-24. doi: 10.1085/jgp.113.1.111. J Gen Physiol. 1999. PMID: 9874692 Free PMC article.
-
Differential occurrence of reluctant openings in G-protein-inhibited N- and P/Q-type calcium channels.J Gen Physiol. 2000 Feb;115(2):175-92. doi: 10.1085/jgp.115.2.175. J Gen Physiol. 2000. PMID: 10653895 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotransmitter modulation of neuronal calcium channels.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2003 Dec;35(6):477-89. doi: 10.1023/b:jobb.0000008021.55853.18. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2003. PMID: 15000517 Review.
Cited by
-
Bile Acid Inhibition of N-type Calcium Channel Currents from Sympathetic Ganglion Neurons.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012 Feb;16(1):25-30. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2012.16.1.25. Epub 2012 Feb 28. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22416216 Free PMC article.
-
Slowed N-type calcium channel (CaV2.2) deactivation by the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor roscovitine.Biophys J. 2005 Sep;89(3):1681-91. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.104.052837. Epub 2005 Jun 10. Biophys J. 2005. PMID: 15951378 Free PMC article.
-
Origin of the voltage dependence of G-protein regulation of P/Q-type Ca2+ channels.J Neurosci. 2008 Dec 24;28(52):14176-88. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1350-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19109500 Free PMC article.
-
G protein modulation of CaV2 voltage-gated calcium channels.Channels (Austin). 2010 Nov-Dec;4(6):497-509. doi: 10.4161/chan.4.6.12871. Epub 2010 Nov 1. Channels (Austin). 2010. PMID: 21150298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
cGMP/protein kinase G-dependent inhibition of N-type Ca2+ channels induced by nitric oxide in human neuroblastoma IMR32 cells.J Neurosci. 2002 Sep 1;22(17):7485-92. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-17-07485.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12196571 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams PR, Jones SW, Pennefather P, Brown DA, Koch C, Lancaster B. Slow synaptic transmission in frog sympathetic ganglia. J Exp Biol. 1986;124:259–285. - PubMed
-
- Bean BP. Neurotransmitter inhibition of neuronal calcium currents by changes in channel voltage dependence. Nature. 1989;340:153–156. - PubMed
-
- Beech DJ, Bernheim L, Hille B. Pertussis toxin and voltage dependence distinguish multiple pathways modulating calcium channels of rat sympathetic neurons. Neuron. 1992;8:97–106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
