Synucleins are developmentally expressed, and alpha-synuclein regulates the size of the presynaptic vesicular pool in primary hippocampal neurons
- PMID: 10777786
- PMCID: PMC6773130
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-09-03214.2000
Synucleins are developmentally expressed, and alpha-synuclein regulates the size of the presynaptic vesicular pool in primary hippocampal neurons
Abstract
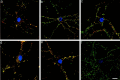
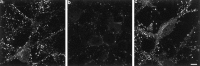
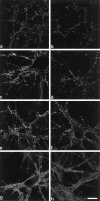
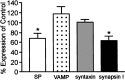
alpha-, beta-, and gamma-Synuclein, a novel family of neuronal proteins, has become the focus of research interest because alpha-synuclein has been increasingly implicated in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease. However, the normal functions of the synucleins are still unknown. For this reason, we characterized alpha-, beta-, and gamma-synuclein expression in primary hippocampal neuronal cultures and showed that the onset of alpha- and beta-synuclein expression was delayed after synaptic development, suggesting that these synucleins may not be essential for synapse formation. In mature cultured primary neurons, alpha- and beta-synuclein colocalized almost exclusively with synaptophysin in the presynaptic terminal, whereas little gamma-synuclein was expressed at all. To assess the function of alpha-synuclein, we suppressed expression of this protein with antisense oligonucleotide technology. Morphometric ultrastructural analysis of the alpha-synuclein antisense oligonucleotide-treated cultures revealed a significant reduction in the distal pool of synaptic vesicles. These data suggest that one function of alpha-synuclein may be to regulate the size of distinct pools of synaptic vesicles in mature neurons.
Figures


References
-
- Abeliovich A, Schmitz Y, Fariñas I, Choi-Lundberg D, Ho W-H, Castillo PE, Shinsky N, Verdugo JMG, Armanini M, Ryan A, Hynes M, Philips H, Sulzer D, Rosenthal A. Mice lacking α-synuclein display functional deficits in the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Neuron. 2000;25:239–252. - PubMed
-
- Banker G, Goslin K. Culturing nerve cells. Cambridge, MA, MIT; 1991.
-
- Benfenati F, Valtorta F, Rubenstein JL, Gorelick FS, Greengard P, Czernik AJ. Synaptic vesicle-associated Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II is a binding protein for synapsin I. Nature. 1992;359:417–420. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
