Reversal of dopamine D(2) receptor responses by an anandamide transport inhibitor
- PMID: 10777802
- PMCID: PMC6773117
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-09-03401.2000
Reversal of dopamine D(2) receptor responses by an anandamide transport inhibitor
Abstract
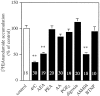
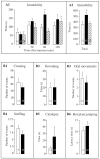
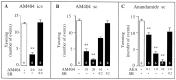
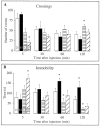
We characterized the pharmacological properties of the anandamide transport inhibitor N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-arachidonamide (AM404) in rats and investigated the effects of this drug on behavioral responses associated with activation of dopamine D(2) family receptors. Rat brain slices accumulated [(3)H]anandamide via a high-affinity transport mechanism that was blocked by AM404. When administered alone in vivo, AM404 caused a mild and slow-developing hypokinesia that was significant 60 min after intracerebroventricular injection of the drug and was reversed by the CB1 cannabinoid receptor antagonist SR141716A. AM404 produced no significant catalepsy or analgesia, two typical effects of direct-acting cannabinoid agonists. However, AM404 prevented the stereotypic yawning produced by systemic administration of a low dose of apomorphine, an effect that was dose-dependent and blocked by SR141716A. Furthermore, AM404 reduced the stimulation of motor behaviors elicited by the selective D(2) family receptor agonist quinpirole. Finally, AM404 reduced hyperactivity in juvenile spontaneously hypertensive rats, a putative model of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. The results support a primary role of the endocannabinoid system in the regulation of psychomotor activity and point to anandamide transport as a potential target for neuropsychiatric medicines.
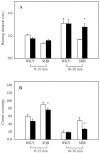
Figures
References
-
- Aspide R, Gironi Carnevale UA, Sergeant JA, Sadile AG. Non-selecive attention and nitric oxide in putative animal models of attention-deficit and hyperactivity disorder. Brain Res. 1998;95:123–133. - PubMed
-
- Baraldi M, Benassi-Benelli A. Apomorphine-induced penile erection in adult rats. Riv Farmacol Terapia. 1975;6:771–772.
-
- Beltramo M, di Tomaso E, Piomelli D. Inhibition of anandamide hydrolysis in rat brain tissue by (E)-6-(bromomethylene) tetrahydro-3-(1-naphthalenyl)-2H-pyran-2-one. FEBS Lett. 1997a;403:263–267. - PubMed
-
- Beltramo M, Stella N, Calignano A, Lin SY, Makriyannis A, Piomelli D. Functional role of high-affinity anandamide transport, as revealed by selective inhibition. Science. 1997b;277:1094–1097. - PubMed
-
- Calignano A, La Rana G, Beltramo M, Makriyannis A, Piomelli D. Potentiation of anandamide hypotension by the transport inhibitor, AM404. Eur J Pharmacol. 1997a;337:R1–R2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
