Calcium-induced calcium release in smooth muscle: loose coupling between the action potential and calcium release
- PMID: 10779321
- PMCID: PMC2217224
- DOI: 10.1085/jgp.115.5.653
Calcium-induced calcium release in smooth muscle: loose coupling between the action potential and calcium release
Abstract
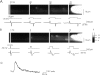
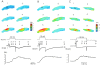
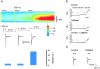
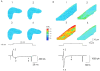
Calcium-induced calcium release (CICR) has been observed in cardiac myocytes as elementary calcium release events (calcium sparks) associated with the opening of L-type Ca(2+) channels. In heart cells, a tight coupling between the gating of single L-type Ca(2+) channels and ryanodine receptors (RYRs) underlies calcium release. Here we demonstrate that L-type Ca(2+) channels activate RYRs to produce CICR in smooth muscle cells in the form of Ca(2+) sparks and propagated Ca(2+) waves. However, unlike CICR in cardiac muscle, RYR channel opening is not tightly linked to the gating of L-type Ca(2+) channels. L-type Ca(2+) channels can open without triggering Ca(2+) sparks and triggered Ca(2+) sparks are often observed after channel closure. CICR is a function of the net flux of Ca(2+) ions into the cytosol, rather than the single channel amplitude of L-type Ca(2+) channels. Moreover, unlike CICR in striated muscle, calcium release is completely eliminated by cytosolic calcium buffering. Thus, L-type Ca(2+) channels are loosely coupled to RYR through an increase in global [Ca(2+)] due to an increase in the effective distance between L-type Ca(2+) channels and RYR, resulting in an uncoupling of the obligate relationship that exists in striated muscle between the action potential and calcium release.
Figures


References
-
- Armstrong C.M., Bezanilla F.M., Horowicz P. Twitches in the presence of ethylene glycol bis(-aminoethyl ether)- N,N′-tetracetic acid. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1972;267:605–608. - PubMed
-
- Arnaudeau S., Boittin F.X., Macrez N., Lavie J.L., Mironneau C., Mironneau J. L-type and Ca2+ release channel-dependent hierarchical Ca2+ signalling in rat portal vein myocytes. Cell Calc. 1997;22:399–411. - PubMed
-
- Berridge M.J. Elementary and global aspects of calcium signalling. J. Exp. Biol. 1997;200:315–319. - PubMed
-
- Bezprozvanny I. Theoretical analysis of calcium wave propagation based on inositol (1,4,5)-trisphosphate (InsP3) receptor functional properties. Cell Calc. 1994;16:151–166. - PubMed
-
- Cannell M.B., Cheng H., Lederer W.J. The control of calcium release in heart muscle. Science. 1995;268:1045–1049. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

