BASC, a super complex of BRCA1-associated proteins involved in the recognition and repair of aberrant DNA structures
- PMID: 10783165
- PMCID: PMC316544
BASC, a super complex of BRCA1-associated proteins involved in the recognition and repair of aberrant DNA structures
Abstract
We report the identities of the members of a group of proteins that associate with BRCA1 to form a large complex that we have named BASC (BRCA1-associated genome surveillance complex). This complex includes tumor suppressors and DNA damage repair proteins MSH2, MSH6, MLH1, ATM, BLM, and the RAD50-MRE11-NBS1 protein complex. In addition, DNA replication factor C (RFC), a protein complex that facilitates the loading of PCNA onto DNA, is also part of BASC. We find that BRCA1, the BLM helicase, and the RAD50-MRE11-NBS1 complex colocalize to large nuclear foci that contain PCNA when cells are treated with agents that interfere with DNA synthesis. The association of BRCA1 with MSH2 and MSH6, which are required for transcription-coupled repair, provides a possible explanation for the role of BRCA1 in this pathway. Strikingly, all members of this complex have roles in recognition of abnormal DNA structures or damaged DNA, suggesting that BASC may serve as a sensor for DNA damage. Several of these proteins also have roles in DNA replication-associated repair. Collectively, these results suggest that BRCA1 may function as a coordinator of multiple activities required for maintenance of genomic integrity during the process of DNA replication and point to a central role for BRCA1 in DNA repair.
Figures
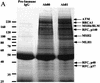



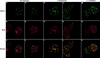

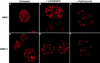

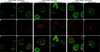
References
-
- Abbott DW, Thompson ME, Robinson-Benion C, Tomlinson G, Jensen RA, Holt JT. BRCA1 expression restores radiation resistance in BRCA1-defective cancer cells through enhancement of transcription-coupled DNA repair. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:18808–18812. - PubMed
-
- Alani E, Lee S, Kane MF, Griffith J, Kolodner RD. Saccharomyces cerevisiae MSH2, a mispaired base recognition protein, also recognizes Holliday junctions in DNA. J Mol Biol. 1997;265:289–301. - PubMed
-
- Allen JB, Zhou Z, Siede W, Friedberg EC, Elledge SJ. The SAD1/RAD53 protein kinase controls multiple checkpoints and DNA damage- induced transcription in yeast. Genes & Dev. 1994;8:2401–2415. - PubMed
-
- Banin S, Moyal L, Shieh S, Taya Y, Anderson CW, Chessa L, Smorodinsky NI, Prives C, Reiss Y, Shiloh Y, Ziv Y. Enhanced phosphorylation of p53 by ATM in response to DNA damage. Science. 1998;281:1674–1677. - PubMed
-
- Bennett RJ, Keck JL, Wang JC. Binding specificity determines polarity of DNA unwinding by the Sgs1 protein of S. cerevisiae. J Mol Biol. 1999;289:235–248. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
