Location of a major susceptibility locus for familial schizophrenia on chromosome 1q21-q22
- PMID: 10784452
- PMCID: PMC3787922
- DOI: 10.1126/science.288.5466.678
Location of a major susceptibility locus for familial schizophrenia on chromosome 1q21-q22
Abstract
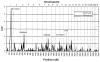
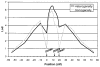
Schizophrenia is a complex disorder, and there is substantial evidence supporting a genetic etiology. Despite this, prior attempts to localize susceptibility loci have produced predominantly suggestive findings. A genome-wide scan for schizophrenia susceptibility loci in 22 extended families with high rates of schizophrenia provided highly significant evidence of linkage to chromosome 1 (1q21-q22), with a maximum heterogeneity logarithm of the likelihood of linkage (lod) score of 6.50. This linkage result should provide sufficient power to allow the positional cloning of the underlying susceptibility gene.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

