Lactic acid permeabilizes gram-negative bacteria by disrupting the outer membrane
- PMID: 10788373
- PMCID: PMC101446
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.66.5.2001-2005.2000
Lactic acid permeabilizes gram-negative bacteria by disrupting the outer membrane
Abstract
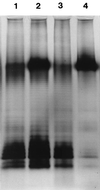
The effect of lactic acid on the outer membrane permeability of Escherichia coli O157:H7, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium was studied utilizing a fluorescent-probe uptake assay and sensitization to bacteriolysis. For control purposes, similar assays were performed with EDTA (a permeabilizer acting by chelation) and with hydrochloric acid, the latter at pH values corresponding to those yielded by lactic acid, and also in the presence of KCN. Already 5 mM (pH 4.0) lactic acid caused prominent permeabilization in each species, the effect in the fluorescence assay being stronger than that of EDTA or HCl. Similar results were obtained in the presence of KCN, except for P. aeruginosa, for which an increase in the effect of HCl was observed in the presence of KCN. The permeabilization by lactic and hydrochloric acid was partly abolished by MgCl(2). Lactic acid sensitized E. coli and serovar Typhimurium to the lytic action of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) more efficiently than did HCl, whereas both acids sensitized P. aeruginosa to SDS and to Triton X-100. P. aeruginosa was effectively sensitized to lysozyme by lactic acid and by HCl. Considerable proportions of lipopolysaccharide were liberated from serovar Typhimurium by these acids; analysis of liberated material by electrophoresis and by fatty acid analysis showed that lactic acid was more active than EDTA or HCl in liberating lipopolysaccharide from the outer membrane. Thus, lactic acid, in addition to its antimicrobial property due to the lowering of the pH, also functions as a permeabilizer of the gram-negative bacterial outer membrane and may act as a potentiator of the effects of other antimicrobial substances.
Figures
References
-
- Aiba Y, Suzuki N, Kabir A M A, Takagi A, Koga Y. Lactic acid-mediated suppression of Helicobacter pylori by the oral administration of Lactobacillus salivarius as a probiotic in a gnotobiotic murine model. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998;93:2097–2101. - PubMed
-
- Baik H S, Bearson S, Dunbar S, Foster J W. The acid tolerance response of Salmonella typhimurium provides protection against organic acids. Microbiology. 1996;142:3195–3200. - PubMed
-
- Cutter C N, Siragusa G R. Population reductions of gram-negative pathogens following treatments with nisin and chelators under various conditions. J Food Prot. 1995;58:977–983. - PubMed
-
- Cutter C N, Siragusa G R. Treatments with nisin and chelators to reduce Salmonella and Escherichia coli on beef. J Food Prot. 1995;58:1028–1030. - PubMed
-
- Daeschel M A, Penner M H. Hydrogen peroxide, lactoperoxidase systems, and reuterin. In: Ray B, Daeschel M, editors. Food preservatives of microbial origin. Boca Raton, Fla: CRC Press; 1992. pp. 155–175.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

