Development of a highly sensitive nested-PCR procedure using a single closed tube for detection of Erwinia amylovora in asymptomatic plant material
- PMID: 10788384
- PMCID: PMC101457
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.66.5.2071-2078.2000
Development of a highly sensitive nested-PCR procedure using a single closed tube for detection of Erwinia amylovora in asymptomatic plant material
Abstract
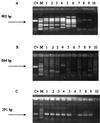
A novel method, which involves a nested PCR in a single closed tube, was developed for the sensitive detection of Erwinia amylovora in plant material. The external and internal primer pairs used had different annealing temperatures and directed the amplification of a specific DNA fragment from plasmid pEA29. The procedure involved two consecutive PCRs, the first of which was performed at a higher annealing temperature that allowed amplification only by the external primer pair. Using pure cultures of E. amylovora, the sensitivity of the nested PCR in one tube was similar to that of a standard nested PCR in two tubes. The specificity and sensitivity were greater than those of standard PCR procedures that used a single primer pair. The presence of inhibitors in plant material, very common in E. amylovora hosts, is overcome with this system in combination with a simple DNA extraction protocol because it eliminates many of the inhibitory compounds. In addition, it needs a very small sample volume (1 microl of DNA extracted). With 83 samples of naturally infected material, this method achieved better results than any other PCR technique: standard PCR detected 55% of positive samples, two-tube nested PCR detected 71% of positive samples, and nested PCR in a single closed tube detected 78% of positive samples. When analyzing asymptomatic plant material, the number of positive samples detected by the developed nested PCR was also the highest, compared with the PCR protocols indicated previously (17, 20, and 25% of 251 samples analyzed, respectively). This method is proposed for the detection of endophytic and epiphytic populations of E. amylovora in epidemiological studies and for routine use in quarantine surveys, due to its high sensitivity, specificity, speed, and simplicity.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sensitive and species-specific detection of Erwinia amylovora by polymerase chain reaction analysis.Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Nov;58(11):3522-6. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.11.3522-3526.1992. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992. PMID: 1482178 Free PMC article.
-
Conventional and real-time PCRs for detection of Erwinia piriflorinigrans allow its distinction from the fire blight pathogen, Erwinia amylovora.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014 Apr;80(8):2390-8. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03626-13. Epub 2014 Feb 7. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24509928 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiation of Erwinia amylovora and Erwinia pyrifoliae strains with single nucleotide polymorphisms and by synthesis of dihydrophenylalanine.Curr Microbiol. 2012 Jul;65(1):73-84. doi: 10.1007/s00284-012-0116-5. Epub 2012 Apr 27. Curr Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22538467
-
Optimization of PCR in application of hot start Taq DNA polymerase for detection of Erwinia amylovora with primers FER1-F and FER1-R.Mikrobiologiia. 2010 Nov-Dec;79(6):819-23. Mikrobiologiia. 2010. PMID: 21446634
-
Identification of the fire blight pathogen, Erwinia amylovora, by PCR assays with chromosomal DNA.Appl Environ Microbiol. 1995 Jul;61(7):2636-42. doi: 10.1128/aem.61.7.2636-2642.1995. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1995. PMID: 7618876 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Potential Role of Rhizobacteria Isolated from Citrus Rhizosphere for Biological Control of Citrus Dry Root Rot.Plants (Basel). 2021 Apr 26;10(5):872. doi: 10.3390/plants10050872. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33926049 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitive detection of RNA viruses associated with gastroenteritis by a hanging-drop single-tube nested reverse transcription-PCR method.J Clin Microbiol. 2002 Nov;40(11):4091-9. doi: 10.1128/JCM.40.11.4091-4099.2002. J Clin Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12409380 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR genotyping as complementary tool for epidemiological surveillance of Erwinia amylovora outbreaks.PLoS One. 2021 Apr 16;16(4):e0250280. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0250280. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33861806 Free PMC article.
-
A novel molecular toolkit for rapid detection of the pathogen and primary vector of thousand cankers disease.PLoS One. 2018 Jan 5;13(1):e0185087. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0185087. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29304036 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative transcriptome analysis of a lowly virulent strain of Erwinia amylovora in shoots of two apple cultivars - susceptible and resistant to fire blight.BMC Genomics. 2017 Nov 13;18(1):868. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-4251-z. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 29132313 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clark G G, Hickey K D, Travis J W. Fireblight management: evaluation of the role of aphids in transmission of bacteria and development of a computerized management system for growers. Penn Fruit News. 1991;71:43–44.
-
- Covey R P, Fischer W R. Timely cutting of fire blight infections reduces losses. Acta Hortic. 1990;273:351–353.
-
- Crepel C, Geenen J, Maes M, Bonn W G. The latent survival of Erwinia amylovora in hibernating shoots. Acta Hortic. 1996;411:21–25.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

