Rapid identification of Yersinia enterocolitica in blood by the 5' nuclease PCR assay
- PMID: 10790127
- PMCID: PMC86632
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.38.5.1953-1958.2000
Rapid identification of Yersinia enterocolitica in blood by the 5' nuclease PCR assay
Abstract
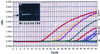
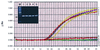
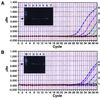
Yersinia enterocolitica accounts for 50% of the clinical sepsis episodes caused by the transfusion of contaminated red blood cells. A 5' nuclease TaqMan PCR assay was developed to detect Y. enterocolitica in blood. Primers and a probe based on the nucleotide sequence of the 16S rRNA gene from Y. enterocolitica were designed. Whole-blood samples were spiked with various numbers of Y. enterocolitica cells, and total chromosomal DNA was extracted. When the TaqMan PCR assay was performed, as few as six bacteria spiked in 200 microliter of blood could be detected. The assay was specific and did not detect other Yersinia species. The TaqMan assay is easy to perform, takes 2 h, and has the potential for use in the rapid detection of Y. enterocolitica contamination in stored blood units.
Figures
References
-
- Akane A, Matsubara K, Nakamura H, Takahashi S, Kimura K. Identification of the heme compound copurified with deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) from bloodstains, a major inhibitor of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification. J Forensic Sci. 1994;39:362–372. - PubMed
-
- Backman A, Lantz P, Radstrom P, Olcen P. Evaluation of an extended diagnostic PCR assay for detection and verification of the common causes of bacterial meningitis in CSF and other biological samples. Mol Cell Probes. 1999;13:49–60. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

