The tight junction protein ZO-1 and an interacting transcription factor regulate ErbB-2 expression
- PMID: 10790369
- PMCID: PMC305688
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.9.2024
The tight junction protein ZO-1 and an interacting transcription factor regulate ErbB-2 expression
Abstract
Epithelial tight junctions regulate paracellular diffusion and restrict the intermixing of apical and basolateral plasma membrane components. We now identify a Y-box transcription factor, ZONAB (ZO-1-associated nucleic acid-binding protein), that binds to the SH3 domain of ZO-1, a submembrane protein of tight junctions. ZONAB localizes to the nucleus and at tight junctions, and binds to sequences of specific promoters containing an inverted CCAAT box. In reporter assays, ZONAB and ZO-1 functionally interact in the regulation of the ErbB-2 promoter in a cell density-dependent manner. In stably transfected overexpressing cells, ZO-1 and ZONAB control expression of endogenous ErbB-2 and function in the regulation of paracellular permeability. These data indicate that tight junctions directly participate in the control of gene expression and suggest that they function in the regulation of epithelial cell differentiation.
Figures
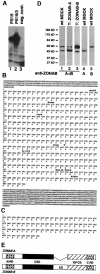

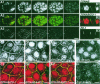
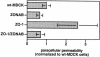
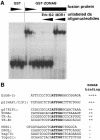


References
-
- Alroy I. and Yarden,Y. (1997) The ErbB signaling network in embryogenesis and oncogenesis: signal diversification through combinatorial ligand–receptor interactions. FEBS Lett., 410, 83–86. - PubMed
-
- Balda M.S. and Anderson,J.M. (1993) Two classes of tight junctions are revealed by ZO-1 isoforms. Am. J. Physiol., 264, C918–C924. - PubMed
-
- Balda M.S. and Matter,K. (1998) Tight junctions. J. Cell Sci., 111, 541–547. - PubMed
-
- Balda M.S., Whitney,J.A., Flores,C., González,S., Cereijido,M. and Matter,K. (1996a) Functional dissociation of paracellular permeability and transepithelial electrical resistance and disruption of the apical–basolateral intramembrane diffusion barrier by expression of a mutant tight junction membrane protein. J. Cell Biol., 134, 1031–1049. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

