Cell cycle-dependent variations in c-Jun and JunB phosphorylation: a role in the control of cyclin D1 expression
- PMID: 10790372
- PMCID: PMC305681
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.9.2056
Cell cycle-dependent variations in c-Jun and JunB phosphorylation: a role in the control of cyclin D1 expression
Abstract
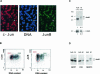
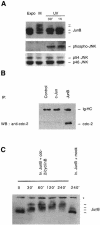
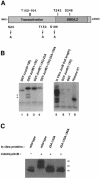
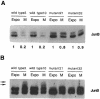
The transcription factor AP-1, composed of Jun and Fos proteins, is a major target of mitogen-activated signal transduction pathways. However, little is known about AP-1 function in normal cycling cells. Here we report that the quantity and the phosphorylation state of the c-Jun and JunB proteins vary at the M-G(1) transition. Phosphorylation of JunB by the p34(cdc2)-cyclin B kinase is associated with lower JunB protein levels in mitotic and early G(1) cells. In contrast, c-Jun levels remain constant while the protein undergoes N-terminal phosphorylation, increasing its transactivation potential. Since JunB represses and c-Jun activates the cyclin D1 promoter, these modifications of AP-1 activity during the M-G(1) transition could provide an impetus for G(1) progression by a temporal increase in cyclin D1 transcription. These findings constitute a novel example of a reciprocal connection between transcription factors and the cell cycle machinery.
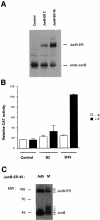
Figures





References
-
- Albanese C., Johnson,J., Watanabe,G., Eklund,N., Vu,D., Arnold,A. and Pestell,R.G. (1995) Transforming p21ras mutants and c-Ets-2 activate the cyclin D1 promoter through distinguishable regions. J. Biol. Chem., 270, 23589–23597. - PubMed
-
- Binetruy B., Smeal,T. and Karin,M. (1991) Ha-Ras augments c-Jun activity and stimulates phosphorylation of its activation domain. Nature, 351, 122–127. - PubMed
-
- Boulikas T. (1995) Phosphorylation of transcription factors and control of the cell cycle. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr., 5, 1–77. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

