Phosphoprotein associated with glycosphingolipid-enriched microdomains (PAG), a novel ubiquitously expressed transmembrane adaptor protein, binds the protein tyrosine kinase csk and is involved in regulation of T cell activation
- PMID: 10790433
- PMCID: PMC2213442
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.191.9.1591
Phosphoprotein associated with glycosphingolipid-enriched microdomains (PAG), a novel ubiquitously expressed transmembrane adaptor protein, binds the protein tyrosine kinase csk and is involved in regulation of T cell activation
Abstract
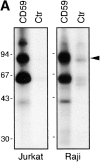
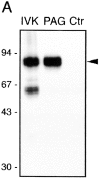
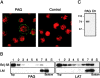
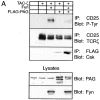
According to a recently proposed hypothesis, initiation of signal transduction via immunoreceptors depends on interactions of the engaged immunoreceptor with glycosphingolipid-enriched membrane microdomains (GEMs). In this study, we describe a novel GEM-associated transmembrane adaptor protein, termed phosphoprotein associated with GEMs (PAG). PAG comprises a short extracellular domain of 16 amino acids and a 397-amino acid cytoplasmic tail containing ten tyrosine residues that are likely phosphorylated by Src family kinases. In lymphoid cell lines and in resting peripheral blood alpha/beta T cells, PAG is expressed as a constitutively tyrosine-phosphorylated protein and binds the major negative regulator of Src kinases, the tyrosine kinase Csk. After activation of peripheral blood alpha/beta T cells, PAG becomes rapidly dephosphorylated and dissociates from Csk. Expression of PAG in COS cells results in recruitment of endogenous Csk, altered Src kinase activity, and impaired phosphorylation of Src-specific substrates. Moreover, overexpression of PAG in Jurkat cells downregulates T cell receptor-mediated activation of the transcription factor nuclear factor of activated T cells. These findings collectively suggest that in the absence of external stimuli, the PAG-Csk complex transmits negative regulatory signals and thus may help to keep resting T cells in a quiescent state.
Figures










References
-
- Tamir I., Cambier J.C. Antigen receptor signalingintegration of protein tyrosine kinase functions. Oncogene. 1998;17:1353–1364. - PubMed
-
- Simons K., Ikonen E. Functional rafts in cell membranes. Nature. 1997;387:569–572. - PubMed
-
- Xavier R., Seed B. Membrane compartmentation and the response to antigen. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1999;11:265–269. - PubMed
-
- Brown D.A., London E. Structure and origin of ordered lipid domains in biological membranes. J. Membr. Biol. 1998;164:103–114. - PubMed
-
- Harder T., Simons K. Caveolae, DIGs, and the dynamics of sphingolipid-cholesterol microdomains. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1997;9:534–542. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

