Focal exocytosis of VAMP3-containing vesicles at sites of phagosome formation
- PMID: 10791982
- PMCID: PMC2174839
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.149.3.697
Focal exocytosis of VAMP3-containing vesicles at sites of phagosome formation
Abstract
Phagocytosis involves the receptor-mediated extension of plasmalemmal protrusions, called pseudopods, which fuse at their tip to engulf a particle. Actin polymerizes under the nascent phagosome and may propel the protrusion of pseudopods. Alternatively, membrane extension could result from the localized insertion of intracellular membranes into the plasmalemma next to the particle. Here we show focal accumulation of VAMP3-containing vesicles, likely derived from recycling endosomes, in the vicinity of the nascent phagosome. Using green fluorescent protein (GFP) as both a fluorescent indicator and an exofacial epitope tag, we show that polarized fusion of VAMP3 vesicles precedes phagosome sealing. It is therefore likely that targeted delivery of endomembranes contributes to the elongation of pseudopods. In addition to mediating pseudopod formation, receptor-triggered focal secretion of endosomes may contribute to polarized membrane extension in processes such as lamellipodial elongation or chemotaxis.
Figures

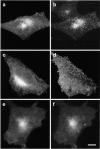
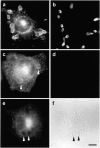
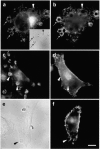

Comment in
-
Quo vadis: polarized membrane recycling in motility and phagocytosis.J Cell Biol. 2000 May 1;149(3):529-30. doi: 10.1083/jcb.149.3.529. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10791966 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Betz W.J., Bewick G.S. Optical analysis of synaptic vesicle recycling at the frog neuromuscular junction. Science. 1992;255:200–203. - PubMed
-
- Bretscher M.S. Getting membrane flow and the cytoskeleton to cooperate in moving cells. Cell. 1996;87:601–606. - PubMed
-
- Buys S.S., Keogh E.A., Kaplan J. Fusion of intracellular membrane pools with cell surfaces of macrophages stimulated by phorbol esters and calcium ionophores. Cell. 1984;38:569–576. - PubMed
-
- Cox D., Tseng C.C., Bjekic G., Greenberg S. A requirement for phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in pseudopod extension. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:1240–1247. - PubMed

