Inverse radiation dose-rate effects on somatic and germ-line mutations and DNA damage rates
- PMID: 10792040
- PMCID: PMC25837
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.090099497
Inverse radiation dose-rate effects on somatic and germ-line mutations and DNA damage rates
Abstract
The mutagenic effect of low linear energy transfer ionizing radiation is reduced for a given dose as the dose rate (DR) is reduced to a low level, a phenomenon known as the direct DR effect. Our reanalysis of published data shows that for both somatic and germ-line mutations there is an opposite, inverse DR effect, with reduction from low to very low DR, the overall dependence of induced mutations being parabolically related to DR, with a minimum in the range of 0.1 to 1.0 cGy/min (rule 1). This general pattern can be attributed to an optimal induction of error-free DNA repair in a DR region of minimal mutability (MMDR region). The diminished activation of repair at very low DRs may reflect a low ratio of induced ("signal") to spontaneous background DNA damage ("noise"). Because two common DNA lesions, 8-oxoguanine and thymine glycol, were already known to activate repair in irradiated mammalian cells, we estimated how their rates of production are altered upon radiation exposure in the MMDR region. For these and other abundant lesions (abasic sites and single-strand breaks), the DNA damage rate increment in the MMDR region is in the range of 10% to 100% (rule 2). These estimates suggest a genetically programmed optimatization of response to radiation in the MMDR region.
Figures
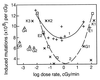
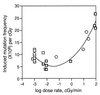

References
-
- United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation. Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation: United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation 1993 Report to the General Assembly. New York: United Nations; 1993.
-
- Hall E J. Int J Radiat Biol. 1991;59:595–610. - PubMed
-
- Amundson S A, Chen D J. Int J Radiat Biol. 1996;69:555–563. - PubMed
-
- Lorenz R, Leuner K, Deubel W, Gollner T, Hempel K. Toxicol Lett. 1993;67:353–363. - PubMed
-
- Thacker J. Adv Radiat Biol. 1992;16:77–165.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

