Cardiovascular effects of melatonin in hypertensive patients well controlled by nifedipine: a 24-hour study
- PMID: 10792199
- PMCID: PMC2014953
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.2000.00195.x
Cardiovascular effects of melatonin in hypertensive patients well controlled by nifedipine: a 24-hour study
Abstract
Aims: As melatonin has been found to play a role in the mechanisms of cardiovascular regulation, we designed the present study to evaluate whether the evening ingestion of the pineal hormone might interfere with the antihypertensive therapy in hypertensive patients well-controlled by nifedipine monotherapy.
Methods: Forty-seven mild to moderate essential hypertensive outpatients taking nifedipine GITS 30 or 60 mg monotherapy at 08.30 h for at least 3 months, were given placebo or melatonin 5 mg at 22.30 h for 4 weeks according to a double-blind cross-over study. At the end of each treatment period patients underwent a 24 h noninvasive ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) during usual working days; sleeping period was scheduled to last from 23.00 to 07.00 h.
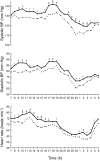
Results: The evening administration of melatonin induced an increase of blood pressure and heart rate throughout the 24 h period (DeltaSBP = + 6.5 mmHg, P < 0.001; DeltaDBP = + 4.9 mmHg, P < 0.01; DeltaHR = + 3.9 beats min-1, P < 0.01). The DBP as well as the HR increase were particularly evident during the morning and the afternoon hours.
Conclusions: We hypothesize that competition between melatonin and nifedipine, is able to impair the antihypertensive efficacy of the calcium channel blocker. This suggests caution in uncontrolled use of melatonin in hypertensive patients. As the pineal hormone might interfere with calcium channel blocker therapy, it cannot be considered simply a dietary supplement.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reduction of cardiovascular structural changes by nifedipine GITS in essential hypertensive patients.Blood Press. 1998 May;7(3):160-9. doi: 10.1080/080370598437376. Blood Press. 1998. PMID: 9758086 Clinical Trial.
-
Dose- and administration time-dependent effects of nifedipine gits on ambulatory blood pressure in hypertensive subjects.Chronobiol Int. 2007;24(3):471-93. doi: 10.1080/07420520701420683. Chronobiol Int. 2007. PMID: 17612946 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative effects of felodipine ER, amlodipine and nifedipine GITS on 24 h blood pressure control and trough to peak ratios in mild to moderate ambulatory hypertension: a forced titration study.Can J Cardiol. 1998 May;14(5):682-8. Can J Cardiol. 1998. PMID: 9627524 Clinical Trial.
-
Current treatment of patients with hypertension: therapeutic implications of INSIGHT.Drugs. 2003;63(14):1435-44. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200363140-00001. Drugs. 2003. PMID: 12834362 Review.
-
Structure and function of small arteries of essential hypertensive patients following chronic treatment with once-a-day nifedipine.Cardiology. 1997;88 Suppl 3:20-6. doi: 10.1159/000177502. Cardiology. 1997. PMID: 9397289 Review.
Cited by
-
Relationship Between Melatonin and Cardiovascular Disease.Cureus. 2021 Jan 27;13(1):e12935. doi: 10.7759/cureus.12935. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 33654615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) and Its Neuroinvasive Capacity: Is It Time for Melatonin?Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Apr;42(3):489-500. doi: 10.1007/s10571-020-00938-8. Epub 2020 Aug 9. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 32772307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Controlled-release oral melatonin supplementation for hypertension and nocturnal hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2022 May;24(5):529-535. doi: 10.1111/jch.14482. Epub 2022 Apr 7. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2022. PMID: 35388609 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin for Insomnia in Medical Inpatients: A Narrative Review.J Clin Med. 2022 Dec 29;12(1):256. doi: 10.3390/jcm12010256. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36615056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effects of melatonin supplementation on blood pressure in patients with metabolic disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Hum Hypertens. 2019 Mar;33(3):202-209. doi: 10.1038/s41371-019-0166-2. Epub 2019 Jan 15. J Hum Hypertens. 2019. PMID: 30647466
References
-
- Cunnane SC, Manku MS, Oka M, Horrobin DF. Enhanced vascular reactivity to various agents following pinealectomy in the rats: role of melatonin. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1980;58:287–293. - PubMed
-
- Zanoboni A, Forni A, Zanobini-muciaccia W, Zanussi C. Effect of pinealectomy on arterial blood pressure and food and water intake in the rat. J Endocrinol Invest. 1978;2:125–130. - PubMed
-
- Zanoboni A, Zanobini-muciaccia W. Experimental hypertension in pinealectomized rats. Life Sci. 1967;6:2327–2331. - PubMed
-
- Karppanen H, Vapatalo H, Lahovara S, Pasonen MK. Pinealectomy-induced hypertension in the rat. Acta Physiol Scand Supplement. 1969;330:94–101.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous