Kinase mutant Btk results in atypical X-linked agammaglobulinaemia phenotype
- PMID: 10792386
- PMCID: PMC1905636
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2000.01230.x
Kinase mutant Btk results in atypical X-linked agammaglobulinaemia phenotype
Abstract
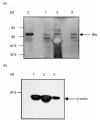
X-linked agammaglobulinaemia (XLA) is a B cell humoral abnormality arising from mutations in the gene encoding Bruton's tyrosine kinase (Btk). The phenotype of XLA can be variable, with some individuals having a less severe immunophenotype, although in most cases this cannot be correlated with the Btk mutation or expression of Btk protein. In this study we describe clinical and immunological heterogeneity within the same pedigree. Analysis of the genetic defect identified a missense mutation in the kinase domain of Btk which, unusually, preserved Btk protein expression but at reduced levels, and also considerably diminished autophosphorylation activity. Structural analysis of the effect of this mutation on the kinase domain suggests that this mutation is not an integral part of the ATP or substrate binding domains but may affect the interaction of the kinase domain with its own kinase domain and other substrates. Together, these data may provide an explanation for the variable XLA phenotype.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Bruton's tyrosine kinase expression and activity in X-linked agammaglobulinaemia (XLA): the use of protein analysis as a diagnostic indicator of XLA.Clin Exp Immunol. 1998 Feb;111(2):334-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1998.00503.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9486400 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation analysis of the Bruton's tyrosine kinase gene in X-linked agammaglobulinemia: identification of a mutation which affects the same codon as is altered in immunodeficient xid mice.Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jan;3(1):161-6. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.1.161. Hum Mol Genet. 1994. PMID: 8162018
-
Deletion within the Src homology domain 3 of Bruton's tyrosine kinase resulting in X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA).J Exp Med. 1994 Aug 1;180(2):461-70. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.2.461. J Exp Med. 1994. PMID: 7519238 Free PMC article.
-
Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) in X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA).Front Biosci. 2000 Dec 1;5:D917-28. doi: 10.2741/vihinen. Front Biosci. 2000. PMID: 11102316 Review.
-
X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA): a genetic tyrosine kinase (Btk) disease.Bioessays. 1996 Oct;18(10):825-34. doi: 10.1002/bies.950181009. Bioessays. 1996. PMID: 8885720 Review.
Cited by
-
Of Mycelium and Men: Inherent Human Susceptibility to Fungal Diseases.Pathogens. 2023 Mar 14;12(3):456. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12030456. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 36986378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Case Report: A Case of X-Linked Agammaglobulinemia With High Serum IgE Levels and Allergic Rhinitis.Front Immunol. 2020 Nov 5;11:582376. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.582376. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33224144 Free PMC article.
-
B cell repertoire in patients with a novel BTK mutation: expanding the spectrum of atypical X-linked agammaglobulinemia.Immunol Res. 2022 Apr;70(2):216-223. doi: 10.1007/s12026-022-09263-2. Epub 2022 Jan 10. Immunol Res. 2022. PMID: 35001352
-
X-linked agammaglobulinemia presenting as polymicrobial pneumonia, including Pneumocystis jirovecii.Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014 Jan;112(1):74-75.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2013.10.008. Epub 2013 Nov 9. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24331399 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Relevance of laboratory testing for the diagnosis of primary immunodeficiencies: a review of case-based examples of selected immunodeficiencies.Clin Mol Allergy. 2011 Apr 9;9:6. doi: 10.1186/1476-7961-9-6. Clin Mol Allergy. 2011. PMID: 21477322 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tsukada S, Saffran DC, Rawlings DJ, et al. Deficient expression of a B cell cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase in human X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Cell. 1993;72:279–90. - PubMed
-
- Vetrie D, Vorechovsky I, Sideras P, et al. The gene involved in X-linked agammaglobulinaemia is a member of the src family of protein-tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1993;361:226–33. - PubMed
-
- Mano H, Yamashita Y, Sato K, Yazaki Y, Hirai H. Tec protein-tyrosine kinase is involved in interleukin-3 signaling pathway. Blood. 1995;85:343–50. - PubMed
-
- Tamagnone L, Lahtinen I, Mustonen T, et al. BMX, a novel nonreceptor tyrosine kinase gene of the BTK/ITK/TEC/TXK family located in chromosome Xp22.2. Oncogene. 1994;9:3683–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

