Regulation of tissue injury responses by the exposure of matricryptic sites within extracellular matrix molecules
- PMID: 10793060
- PMCID: PMC1876929
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65020-1
Regulation of tissue injury responses by the exposure of matricryptic sites within extracellular matrix molecules
Abstract
Extracellular matrix (ECM) is known to provide signals controlling cell shape, migration, proliferation, differentiation, morphogenesis, and survival. Recent data shows that some of these signals are derived from biologically active cryptic sites within matrix molecules (matricryptic sites) that are revealed after structural or conformational alteration of these molecules. We propose the name, matricryptins, for enzymatic fragments of ECM containing exposed matricryptic sites. Mechanisms regulating the exposure of matricryptic sites within ECM molecules include the major mechanism of enzymatic breakdown as well as others including ECM protein multimerization, adsorption to other molecules, cell-mediated mechanical forces, and ECM denaturation. Such matrix alterations occur during or as a result of tissue injury, and thus, the appearance of matricryptic sites within an injury site may provide important new signals to regulate the repair process. Here, we review the data supporting this concept and provide insight into why the increased exposure of matricryptic sites may be an important regulatory step in tissue responses to injury.
Figures


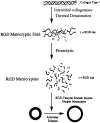
References
-
- Lukashev ME, Werb Z: ECM signalling: orchestrating cell behaviour and misbehaviour. Trends Cell Biol 1998, 8:437-441 - PubMed
-
- Ruoslahti E: Fibronectin and its integrin receptors in cancer. Adv Cancer Res 1999, 76:1-20 - PubMed
-
- Hynes RO: Integrins: versatility, modulation and signalling in cell adhesion. Cell 1992, 69:11-25 - PubMed
-
- Shrivastava A, Radziejewski C, Campbell E, Kovac L, McGlynn M, Ryan TE, Davis S, Goldfarb MP, Glass DJ, Lemke G, Yancopoulos GD: An orphan receptor tyrosine kinase family whose members serve as nonintegrin collagen receptors. Mol Cell 1997, 1:25-34 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

