Contribution of apoptosis and apoptosis-related proteins to the malformation of the primitive intrahepatic biliary system in Meckel syndrome
- PMID: 10793071
- PMCID: PMC1876920
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65031-6
Contribution of apoptosis and apoptosis-related proteins to the malformation of the primitive intrahepatic biliary system in Meckel syndrome
Abstract
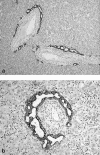
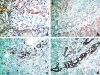
In the developing liver, the complete or partial persistence of the primitive double-layered cylinder of biliary-type cells that surrounds the branches of portal vein and its mesenchyme gives origin to portal tracts with an increased number of bile duct structures. The term "ductal plate malformation of the liver" was coined to label the insufficient remodeling of the primitive intrahepatic biliary system. Meckel syndrome is an autosomal recessive inherited disease characterized by occipital encephalocele, postaxial polydactyly, diffuse cystic renal dysplasia, and malformation of the ductal plate of the liver. We studied 52 fetuses with Meckel syndrome from five German centers (Berlin, Freiburg, Heidelberg, Mainz, and Marburg). Analysis of apoptosis and cell proliferation (Ki-67) was performed by terminal deoxynucleotide transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL) and immunohistochemistry in the liver of 24 normal fetuses of different gestational ages (14-38 weeks of gestation) and in 14 fetuses with Meckel syndrome (17-38 weeks of gestation). The expression of two apoptosis-related proteins, Fas (a transmembrane cell surface protein involved in the apoptosis) and Bcl-2 (an anti-apoptotic protein), was studied by immunohistochemistry in the liver of 11 normal fetuses of different gestational ages (14-40 weeks of gestation) and in 40 fetuses with Meckel syndrome (16-38 weeks of gestation). In control fetuses, apoptosis rate and cell proliferation were high in the remodeling ductal plate and moderate in the ductal plate and in remodeled bile ducts. During gestation, expression of Fas and Bcl-2 decreased and increased, respectively. The malformed ductal plates in the fetal livers with Meckel syndrome showed a marked decrease in the apoptotic rate and Fas expression and an increase in proliferative activity and Bcl-2 expression in comparison with control fetuses. Furthermore, by linear regression analysis, we found that both proliferation activity and apoptosis rate in the ductal plate malformation of fetuses with Meckel syndrome were practically constant along the gestation. These results, which represent the first systematic study of apoptosis in ductal plate malformation of the liver, indicate that 1) animals harboring the gene defect of Meckel syndrome could be a good model for the study of the abnormal development of the primitive intrahepatic biliary system, 2) a decreased cell turnover occurs in the ductal plate malformation of fetuses with Meckel syndrome, and 3) the increase of Bcl-2 expression contributes to the pathogenesis of the lack of remodeling of ductal plate of the liver in Meckel syndrome.
Figures



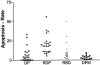




References
-
- Zou H, Niswander L: Requirement for BMP signaling in interdigital apoptosis and scale formation. Science 1996, 272:738-741 - PubMed
-
- Desmet VJ: Intrahepatic bile ducts under the lens. J Hepatol 1985, 1:545-559 - PubMed
-
- Blankenberg TA, Lund JK, Reubner BH: Normal and abnormal development of human intrahepatic bile ducts: an immunohistochemical perspective. Perspect Pediatr Pathol 1991, 14:143-167 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

