Expression of agrin, dystroglycan, and utrophin in normal renal tissue and in experimental glomerulopathies
- PMID: 10793086
- PMCID: PMC1876919
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65046-8
Expression of agrin, dystroglycan, and utrophin in normal renal tissue and in experimental glomerulopathies
Abstract
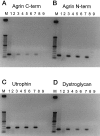
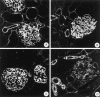
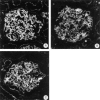
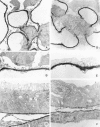
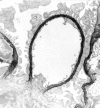
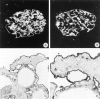
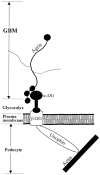
The dystrophin-glycoprotein complex, which comprises alpha- and beta-dystroglycan, sarcoglycans, and utrophin/dystrophin, links the cytoskeleton to agrin and laminin in the basal lamina in muscle and epithelial cells. Recently, agrin was identified as a major heparan sulfate proteoglycan in the glomerular basement membrane. In the present study, we found mRNA expression for agrin, dystroglycan, and utrophin in kidney cortex, isolated glomeruli, and cultured podocytes and mesangial cells. In immunofluorescence, agrin was found in the glomerular basement membrane. The antibodies against alpha- and beta-dystroglycan and utrophin revealed a granular podocyte-like staining pattern along the glomerular capillary wall. With immunoelectron microscopy, agrin was found in the glomerular basement membrane, dystroglycan was diffusely found over the entire cell surface of the podocytes, and utrophin was localized in the cytoplasm of the podocyte foot processes. In adriamycin nephropathy, a decrease in the glomerular capillary wall staining for dystroglycan was observed probably secondary to the extensive fusion of foot processes. Immunoelectron microscopy showed a different distribution pattern as compared to the normal kidney, with segmentally enhanced expression of dystroglycan at the basal side of the extensively fused podocyte foot processes. In passive Heymann nephritis we observed no changes in the staining intensity and distribution of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex by immunofluorescence and immunoelectron microscopy. From these data, we conclude that agrin, dystroglycan, and utrophin are present in the glomerular capillary wall and their ultrastructural localization supports the concept that these molecules are involved in linking the podocyte cytoskeleton to the glomerular basement membrane.
Figures


References
-
- Henry MD, Campbell KP: Dystroglycan: an extracellular matrix receptor linked to the cytoskeleton. Curr Opin Cell Biol 1996, 8:625-631 - PubMed
-
- Campbell KP: Three muscular dystrophies: loss of cytoskeleton-extracellular matrix linkage. Cell 1995, 80:675-679 - PubMed
-
- Worton R: Muscular dystrophies: diseases of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex. Science 1995, 270:755-756 - PubMed
-
- Ervasti JM, Ohlendieck K, Kahl SD, Gaver MG, Campbell KP: Deficiency of a glycoprotein component of the dystrophin complex in dystrophic muscle. Nature 1990, 345:315-319 - PubMed
-
- Cote PD, Moukhles H, Lindenbaum M, Carbonetto S: Chimaeric mice deficient in dystroglycans develop muscular dystrophy and have disrupted myoneural synapses. Nat Genet 1999, 23:338-342 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

