Reduced leptin levels in starvation increase susceptibility to endotoxic shock
- PMID: 10793089
- PMCID: PMC1876910
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65049-3
Reduced leptin levels in starvation increase susceptibility to endotoxic shock
Abstract
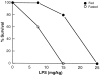
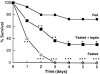
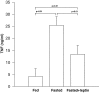
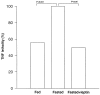
Malnutrition compromises immune function, reducing resistance to infection. We examine whether the decrease in leptin induced by starvation increases susceptibility to lipopolysaccharide (LPS)- and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-induced lethality. In mice, fasting for 48 hours enhances sensitivity to LPS. Decreasing the fasting-induced fall in leptin by leptin administration markedly reduced sensitivity to LPS. Although fasting decreases basal leptin levels, LPS treatment increased leptin to the same extent as in fed animals. Fasting increased basal serum corticosterone; leptin treatment blunted this increase. Fasting decreased the ability of LPS to increase corticosterone; leptin restored the corticosterone response to LPS. Serum glucose levels were decreased in fasted mice and LPS induced a further decrease. Leptin treatment affected neither basal glucose nor that after LPS. LPS induced a fivefold greater increase in serum TNF in fasted mice, which was blunted by leptin replacement. In contrast, LPS induced lower levels of interferon-gamma and no differences in interleukin-1beta in fasted compared to fed animals; leptin had no effect on those cytokines. Furthermore, fasting increased sensitivity to the lethal effect of TNF itself, which was also reversed by leptin treatment. Thus, leptin seems to be protective by both inhibiting TNF induction by LPS and by reducing TNF toxicity.
Figures
References
-
- Friedman JM, Halaas JL: Leptin and the regulation of body weight in mammals. Nature 1998, 395:763-770 - PubMed
-
- Frederich RC, Hamann A, Anderson S, Lollmann B, Lowell BB, Flier JS: Leptin levels reflect body lipid content in mice: evidence for diet- induced resistance to leptin action. Nat Med 1995, 1:1311-1314 - PubMed
-
- Maffei M, Halaas J, Ravussin E, Pratley RE, Lee GH, Zhang Y, Fei H, Kim S, Lallone R, Ranganathan S, Kern PA, Friedman JM: Leptin levels in human and rodent: measurement of plasma leptin and ob RNA in obese and weight-reduced subjects. Nat Med 1995, 1:1155-1161 - PubMed
-
- Ahima RS, Prabakaran D, Mantzoros C, Qu D, Lowell B, Maratos-Flier E, Flier JS: Role of leptin in the neuroendocrine response to fasting. Nature 1996, 382:250-252 - PubMed
-
- Schwartz MW, Seeley RJ: Seminars in medicine of the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center. Neuroendocrine responses to starvation and weight loss. N Engl J Med 1997, 336:1802-1811 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

