Azathioprine for rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 10796441
- PMCID: PMC8406472
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001461
Azathioprine for rheumatoid arthritis
Update in
-
Azathioprine for treating rheumatoid arthritis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000;(4):CD001461. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001461. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000. PMID: 11034720
Abstract
Objectives: To assess the short-term effects of azathioprine for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Search strategy: We searched the Cochrane Musculoskeletal Group's trials register, the Cochrane Controlled Trials Register, Medline up to and including July 1998 and Embase from 1988-1998. We also carried out a handsearch of the reference lists of the trials retrieved from the electronic search.
Selection criteria: All randomized controlled trials and controlled clinical trials comparing azathioprine against placebo in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Data collection and analysis: Data was extracted independently by two reviewers (CS, EB); disagreements were resolved by discussion or third party adjudication (MS). The same reviewers (CS, EB) assessed the methodological quality of the trials using a validated quality assessment tool. Rheumatoid arthritis outcome measures were extracted from the publications for the six-month endpoint. The pooled analysis was performed using standardized mean differences for joint counts, pain and functional status assessments. Weighted mean differences were used for erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). Toxicity was evaluated with pooled odds ratios for withdrawals and for adverse reactions. The 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) are presented. A chi-square test was used to assess heterogeneity among trials. Fixed effects models were used throughout, since no statistical heterogeneity was found.
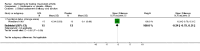
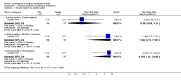
Main results: Three trials with a total of 81 patients were included in the analysis. Forty patients were randomized to azathioprine and forty-one to placebo. A pooled estimate was calculated for two outcomes. A statistically significant benefit was observed for azathioprine when compared to placebo for tender joint scores. The standardized weighted mean difference between treatment and placebo was -0.98 (95% CI -1.45, -0.50). Withdrawals from adverse reactions were significantly higher in the azathioprine group OR=4.56 (95% CI 1.16, 17.85).
Reviewer's conclusions: Azathioprine appears to have a statistically significant benefit on the disease activity in joints of patients with RA. This evidence however is based on a small number of patients, included in older trials. Its effects on long-term functional status and radiological progression were not assessed due to lack of data. Toxicity is shown to be higher and more serious than that observed with other disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs). Given this high risk to benefit ratio, there is no evidence to recommend the use of azathioprine over other DMARDs.
Conflict of interest statement
None known
Figures




References
References to studies included in this review
Levy 1972 {published data only}
-
- Levy J, Paulus HE, Barnett EV, Sokoloff M, Bangert R, & Pearson CM. A double‐blind controlled evaluation of azathioprine treatment in rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatism 1972;15(1):116‐7.
Urowitz 1973 {published data only}
-
- Urowitz MB, Gordon DA, Smythe HA, Pruzanski W, & Ogryzlo MA. Azathioprine in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis & Rheum 1973;16:411‐418. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Barnes 1969 {published data only}
Cade 1976 {published data only}
-
- Cade R, Stein G, Pickering M, Schlein E, Spooner G. Low dose, long term treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with azathioprine. Southern Medical Journal 1976;69(4):388‐392. - PubMed
De Silva 1981 {published data only}
Dixon 1971 {published data only}
Goebel 1976 {published data only}
-
- Goebel KM, Janzen KJ, & Borngen U. Disparity between clinical and immune responses in a controlled trial of azathioprine in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 1976;9:405‐410. - PubMed
Heurkens 1991 {published data only}
-
- Heurkens AHM, Westedt ML, Breedveld FC. Prednisone plus azathioprine treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis complicated by vasculitis. Arch Intern Med 1991;151:2249‐54. - PubMed
Levy 1975 {published data only}
-
- Levy J, Paulus HE, Bangert R. Comparison of azathioprine and cyclophosphamide in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis & Rheum 1975;18:412‐413.
Mason 1969 {published data only}
Nicholls 1973 {published data only}
Pedersen 1984 {published data only}
-
- Pedersen BK, Beyer JM, Rasmussen A, Klarlund K, Horslev‐Petersen K, Pedersen BN, & Helin P. Azathioprine as single drug in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis induces complete suppresion of natural killer cell activity. Acta Path Microbiol Immunol Scand 1984;Sect C 92:221‐225. - PubMed
Additional references
Clark 1998
Dwosh 1977
-
- Dwosh IL, Stein HB, Urowitz MB, Smythe HA, Hunter T, Ogryzlo MA. Azathioprine in early rheumatoid arthritis. Comparison with gold and chloroquine. Arthritis Rheum 1977;20(2):685‐92. - PubMed
Felson 1993
-
- Felson DT, Anderson JJ, Boers M, et al. The American College of Rheumatology preliminary core set of disease activity measures for rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials. Arthritis Rheum 1993;36:729‐40. - PubMed
Halberg 1984
-
- Halberg P, Bentzon MW, Crohn O, et al. Double‐blind trial of levamisole, penicillamine and azathioprine in rheumatoid arthritis. Danish Med Bull 1984;31:403‐9. - PubMed
Jadad 1996
-
- Jadad A, Moore A, Carrol D, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized trials: is blinding necessary?. Control Clin Trial 1996;17:1‐12. - PubMed
Jeurissen 1991
-
- Jeurissen MEC, Boerbooms AMTh, Putte LBA, Doesburg WH, Lemmens A. Influence of methotrexate and azathioprine on radiologic progression in rheumatoid arthritis. Arandomized double‐blind study. Ann Int Med 1991;114:999‐1004. - PubMed
Kazis 1989
-
- Kazis LEE, Anderson JJ, Meenan RF. Effect sizes for interpreting changes in health status. Medical Care 1989;27(S3):S178‐89. - PubMed
OMERACT 1993
-
- OMERACT. Conference on Outcome Measures in Rheumatoid Arthritis Clinical Trials. J Rheumatol 1993;20:526‐91. - PubMed
Paulus 1984
-
- Paulus HE, Williams HJ, Ward JR, et al. Azathioprine versus d‐penicillamine in rheumatoid arthritis patients who have been treated unsuccesfully with gold. Arthritis Rheum 1984;27:721‐7. - PubMed
Singh 1989
-
- Singh G, Fries JF, Spitz PW, Williams CA. Azathioprine toxicity in rheumatoid arthritis: a national post‐marketing perspective. Arthritis Rheum 1989:a national post‐marketing perspective. Arthritis Rheum 1989;837‐43. - PubMed
Suarez‐Almazor 1998a
-
- Suarez‐Almazor ME, Belseck E, Shea B, Homik J, Wells G, Tugwell P. Rheumatoid arthritis: Antimalarials for treating rheumatoid arthritis. Cochrane Data Base of Systematic Reviews 1998, Oxford, UK. - PubMed
Suarez‐Almazor 1998b
-
- Suarez‐Almazor ME, Belseck E, Shea B, Wells G, Tugwell P. Rheumatoid arthritis: Cyclophosphamide for treating rheumatoid arthritis. Cochrane Data Base of Systematic Reviews 1998, Oxford, UK. - PubMed
Suarez‐Almazor 1998d
Suarez‐Almazor 1999c
-
- Suarez‐Almazor ME, Belseck E, Shea B, Wells G, Tugwell P. Rheumatoid arthritis: Methotrexate vs. placebo [Methotrexate for treating rheumatoid arthritis]. Cochrane Data Base of Systematic Reviews 1999, Oxford, UK.
Wells 1998
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

