Antibody response of patients with Helicobacter pylori-related gastric adenocarcinoma: significance of anti-cagA antibodies
- PMID: 10799462
- PMCID: PMC95895
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.7.3.463-467.2000
Antibody response of patients with Helicobacter pylori-related gastric adenocarcinoma: significance of anti-cagA antibodies
Abstract
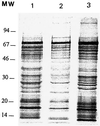
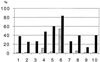
The aim of this study was to search for a specific antibody pattern in sera from patients suffering from Helicobacter pylori-related gastric adenocarcinoma (GAC). The serological response of 22 patients suffering from GAC, 31 patients with gastroduodenal ulcer, and 39 asymptomatic subjects was analyzed using immunoblotting performed with three H. pylori strains: strain ATCC 43579; strain B110, isolated from a patient with ulcers; and strain B225, isolated from a patient with GAC. In addition, the latex agglutination test Pyloriset Dry was used to analyze ambiguous sera. H. pylori seropositivity was 75% in the GAC group, 61.3% in the ulcer group, and 56.4% in the asymptomatic group. Anti-CagA antibodies were found more often in the GAC group (48.8%) and in the ulcer group (47.3%) than in the asymptomatic group (21.2%). These percentages depended on the strain used as an antigen: in the GAC group, the anti-CagA frequencies were 93.3, 40, and 13.3% with strains B225, B110, and ATCC 43579, respectively. Thus the presence of anti-CagA antibodies was increased in patients suffering from H. pylori-related GAC, in particular when the CagA antigen was from a GAC strain. These data suggest the existence of a CagA protein specifically expressed by H. pylori strains isolated from GAC patients.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A CagA-independent cluster of antigens related to the risk of noncardia gastric cancer: associations between Helicobacter pylori antibodies and gastric adenocarcinoma explored by multiplex serology.Int J Cancer. 2014 Jun 15;134(12):2942-50. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28621. Epub 2013 Dec 3. Int J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24259284
-
Seroprevalence of eight Helicobacter pylori antigens among 182 patients with peptic ulcer, MALT gastric lymphoma or non-ulcer dyspepsia. Higher rate of seroreactivity against CagA and 35-kDa antigens in patients with peptic ulcer originating from Europe and Africa.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1999 Jul;11(7):721-6. doi: 10.1097/00042737-199907000-00007. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1999. PMID: 10445790
-
Clinical relevance of CagA-specific antibodies related to CagA status of Helicobacter pylori isolates using immunofluorescence test and PCR.Infection. 2001 May-Jun;29(3):154-8. doi: 10.1007/s15010-001-1102-1. Infection. 2001. PMID: 11440386
-
H. pylori and cagA: relationships with gastric cancer, duodenal ulcer, and reflux esophagitis and its complications.Helicobacter. 1998 Sep;3(3):145-51. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-5378.1998.08031.x. Helicobacter. 1998. PMID: 9731983 Review.
-
The role of CagA status in gastric and extragastric complications of Helicobacter pylori.J Physiol Pharmacol. 1999 Dec;50(5):833-45. J Physiol Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10695563 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the role of H pylori infection in pathogenesis of gastric cancer by immunoblot assay.World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Nov 21;12(43):7029-32. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i43.7029. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 17109500 Free PMC article.
-
Development of an in-house enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay based on surface whole cell antigen for diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with gastroduodenal ulcer disease.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014 Jan;30(1):305-15. doi: 10.1007/s11274-013-1448-4. Epub 2013 Aug 7. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 23921679
-
Is Helicobacter Pylori an endogenous source of diethyl phthalate in humans?Environ Res. 2014 Oct;134:402-4. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2014.08.019. Epub 2014 Sep 22. Environ Res. 2014. PMID: 25218706 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles in Helicobacter pylori-mediated diseases: mechanisms and therapeutic potential.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Feb 11;23(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02074-6. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 39934861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of Helicobacter pylori vacA and cagA genotypes and host serological response.J Clin Microbiol. 2001 Apr;39(4):1339-44. doi: 10.1128/JCM.39.4.1339-1344.2001. J Clin Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11283053 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asaka M, Kudo M, Kato M, Sugiyama T, Takeda H. Long term Helicobacter pylori infection from gastritis to gastric cancer. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1998;12:9–15. - PubMed
-
- Atherton J C, Cao P, Peek R M, Jr, Tummuru M K, Blaser M J, Cover T L. Mosaicism in vacuolation cytotoxin alleles of Helicobacter pylori. Association of vacA types with cytotoxin production and peptic ulceration. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:17771–17777. - PubMed
-
- Baron J H, Logan R P H. Infection by Helicobacter pylori is the major cause of duodenal ulcer. Proc R Coll Physicians Edinb. 1994;24:21–36.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

