Modulation of Dengue virus infection in human cells by alpha, beta, and gamma interferons
- PMID: 10799569
- PMCID: PMC110847
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.11.4957-4966.2000
Modulation of Dengue virus infection in human cells by alpha, beta, and gamma interferons
Abstract
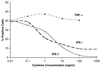
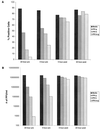
A role for interferon (IFN) in modulating infection by dengue virus (DV) has been suggested by studies in DV-infected patients and IFN receptor-deficient mice. To address how IFN modulates DV type 2 infection, we have assayed IFN-alpha, -beta, and -gamma for the ability to enhance or diminish antibody-independent and antibody-dependent cell infection using a competitive, asymmetric reverse transcriptase-mediated PCR (RT-PCR) assay that quantitates positive and negative strands of viral RNA, a flow cytometric assay that measures viral antigen, and a plaque assay that analyzes virion production. Our data suggest that IFN-alpha and -beta protect cells against DV infection in vitro. Treatment of hepatoma cells with IFN-alpha or -beta decreases viral RNA levels greater than 1, 000-fold, the percentage of cells infected 90 to 95%, and the amount of infectious virus secreted 150- to 100,000-fold. These results have been reproduced with several cell types and viral strains, including low-passage isolates. In contrast, IFN-gamma has a more variable effect depending on the cell type and pathway of infection. Quantitative RT-PCR experiments indicate that IFN inhibits DV infection by preventing the accumulation of negative-strand viral RNA.
Figures






References
-
- Balmaseda A, Sandoval E, Perez L, Gutierrez C M, Harris E. Application of molecular typing techniques in the 1998 dengue epidemic in Nicaragua. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1999;61:893–897. - PubMed
-
- Bielefeldt-Ohmann H. Analysis of antibody-independent binding of dengue viruses and dengue virus envelope protein to human myelomonocytic cells and B lymphocytes. Virus Res. 1998;57:63–79. - PubMed
-
- Boehm U, Klamp T, Groot M, Howard J C. Cellular responses to interferon-gamma. Annu Rev Immunol. 1997;15:749–795. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Maguire T, Hileman R E, Fromm J R, Esko J D, Linhardt R J, Marks R M. Dengue virus infectivity depends on envelope protein binding to target cell heparan sulfate. Nat Med. 1997;3:866–871. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

