Distribution, targeting, and internalization of the sst4 somatostatin receptor in rat brain
- PMID: 10804219
- PMCID: PMC6772697
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-10-03785.2000
Distribution, targeting, and internalization of the sst4 somatostatin receptor in rat brain
Abstract
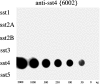
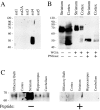
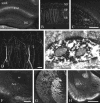
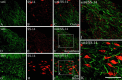
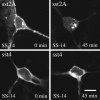
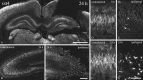
Somatostatin mediates its diverse physiological effects through a family of five G-protein-coupled receptors (sst(1)-sst(5)); however, knowledge about the distribution of individual somatostatin receptor proteins in mammalian brain is incomplete. In the present study, we have examined the regional and subcellular distribution of the somatostatin receptor sst(4) in the rat CNS by raising anti-peptide antisera to the C-terminal tail of sst(4). The specificity of affinity-purified antibodies was demonstrated using immunofluorescent staining of HEK 293 cells stably transfected with an epitope-tagged sst(4) receptor. In Western blotting, the antiserum reacted specifically with a broad band in rat brain, which migrated at approximately 70 kDa before and approximately 50 kDa after enzymatic deglycosylation. sst(4)-Like immunoreactivity was most prominent in many forebrain regions, including the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, striatum, amygdala, and hypothalamus. Analysis at the electron microscopic level revealed that sst(4)-expressing neurons target this receptor preferentially to their somatodendritic domain. Like the sst(2A) receptor, sst(4)-immunoreactive dendrites were often closely apposed by somatostatin-14-containing fibers and terminals. However, unlike the sst(2A) receptor, sst(4) was not internalized in response to intracerebroventricular administration of somatostatin-14. After percussion trauma of the cortex, neuronal sst(4) receptors progressively declined at the sites of damage. This decline coincided with an induction of sst(4) expression in cells with a glial-like morphology. Together, this study provides the first description of the distribution of immunoreactive sst(4) receptor proteins in rat brain. We show that sst(4) is strictly somatodendritic and most likely functions in a postsynaptic manner. In addition, the sst(4) receptor may have a previously unappreciated function during the neuronal degeneration-regeneration process.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Immunohistochemical distribution of the somatostatin receptor subtype 5 in the adult rat brain: predominant expression in the basal forebrain.J Comp Neurol. 1999 Sep 13;412(1):69-82. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-9861(19990913)412:1<69::aid-cne5>3.0.co;2-v. J Comp Neurol. 1999. PMID: 10440710
-
Immunohistochemical localization of the somatostatin sst(4) receptor in rat brain.Neuroscience. 2000;98(3):523-33. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(00)00147-0. Neuroscience. 2000. PMID: 10869846
-
Development of selective antibodies against the human somatostatin receptor subtypes sst1-sst5.Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1997 Oct 3;49(1-2):82-8. doi: 10.1016/s0169-328x(97)00127-7. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1997. PMID: 9387866
-
Localization of five somatostatin receptors in the rat central nervous system using subtype-specific antibodies.J Physiol Paris. 2000 May-Aug;94(3-4):259-64. doi: 10.1016/s0928-4257(00)00212-6. J Physiol Paris. 2000. PMID: 11088003 Review.
-
Somatostatin and its receptor family.Front Neuroendocrinol. 1999 Jul;20(3):157-98. doi: 10.1006/frne.1999.0183. Front Neuroendocrinol. 1999. PMID: 10433861 Review.
Cited by
-
Ligand internalization and recycling by human recombinant somatostatin type 4 (h sst(4)) receptors expressed in CHO-K1 cells.Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Mar;132(5):1102-10. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703896. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11226141 Free PMC article.
-
Somatostatin increases rat locomotor activity by activating sst(2) and sst (4) receptors in the striatum and via glutamatergic involvement.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2009 Feb;379(2):181-9. doi: 10.1007/s00210-008-0346-z. Epub 2008 Sep 3. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 18766327
-
Activation of somatostatin receptors in the globus pallidus increases rat locomotor activity and dopamine release in the striatum.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2008 Dec;201(3):413-22. doi: 10.1007/s00213-008-1305-6. Epub 2008 Sep 3. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2008. PMID: 18766330
-
Expression of Somatostatin Receptor Subtypes (SSTR-1-SSTR-5) in Pediatric Hematological and Oncological Disorders.Molecules. 2020 Dec 7;25(23):5775. doi: 10.3390/molecules25235775. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33297556 Free PMC article.
-
Agonists, Antagonists and Receptors of Somatostatin: Pathophysiological and Therapeutical Implications in Neoplasias.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Sep 2;46(9):9721-9759. doi: 10.3390/cimb46090578. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39329930 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bell GI, Reisine T. Molecular biology of somatostatin receptors. Trends Neurosci. 1993;16:34–38. - PubMed
-
- Bito H, Mori M, Sakanaka C, Takano T, Honda Z, Gotoh Y, Nishida E, Shimizu T. Functional coupling of SSTR4, a major hippocampal somatostatin receptor, to adenylate cyclase inhibition, arachidonate release, and activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:12722–12730. - PubMed
-
- Brazeau P, Vale W, Burgus R, Ling N, Butcher M, Rivier J, Guillemin R. Hypothalamic polypeptide that inhibits the secretion of immunoreactive pituitary growth hormone. Science. 1973;179:77–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
