Projections from the rat prefrontal cortex to the ventral tegmental area: target specificity in the synaptic associations with mesoaccumbens and mesocortical neurons
- PMID: 10804226
- PMCID: PMC6772693
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-10-03864.2000
Projections from the rat prefrontal cortex to the ventral tegmental area: target specificity in the synaptic associations with mesoaccumbens and mesocortical neurons
Abstract
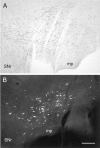
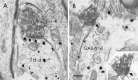
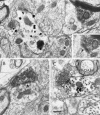
Excitatory projections from the prefrontal cortex (PFC) to the ventral tegmental area (VTA) play an important role in regulating the activity of VTA neurons and the extracellular levels of dopamine (DA) within forebrain regions. Previous investigations have demonstrated that PFC terminals synapse on the dendrites of DA and non-DA neurons in the VTA. However, the projection targets of these cells are not known. To address whether PFC afferents innervate different populations of VTA neurons that project to the nucleus accumbens (NAc) or to the PFC, a triple labeling method was used that combined peroxidase markers for anterograde and retrograde tract-tracing with pre-embedding immunogold-silver labeling for either tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) or GABA. Within the VTA, PFC terminals formed asymmetric synapses onto dendritic shafts that were immunoreactive for either TH or GABA. PFC terminals also synapsed on VTA dendrites that were retrogradely labeled from the NAc or the PFC. Dendrites retrogradely labeled from the NAc and postsynaptic to PFC afferents were sometimes immunoreactive for GABA but were never TH-labeled. Conversely, dendrites retrogradely labeled from the PFC and postsynaptic to PFC afferents were sometimes immunoreactive for TH but were never GABA-labeled. These results provide the first demonstration of PFC afferents synapsing on identified cell populations in the VTA and indicate a considerable degree of specificity in the targets of the PFC projection. The unexpected finding of selective PFC synaptic input to GABA-containing mesoaccumbens neurons and DA-containing mesocortical neurons suggests novel mechanisms through which the PFC can influence the activity of ascending DA and GABA projections.
Figures




References
-
- Bertolino A, Knable MB, Saunders RC, Callicott JH, Kolachana B, Mattay VS, Bachevalier J, Frank JA, Egan M, Weinberger DR. The relationship between dorsolateral prefrontal N-acetylaspartate measures and striatal dopamine activity in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry. 1999;45:660–667. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
