Three yeast proteins related to the human candidate tumor suppressor p33(ING1) are associated with histone acetyltransferase activities
- PMID: 10805724
- PMCID: PMC85704
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.11.3807-3816.2000
Three yeast proteins related to the human candidate tumor suppressor p33(ING1) are associated with histone acetyltransferase activities
Abstract
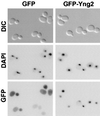
Three Saccharomyces cerevisiae proteins (Yng1/YOR064c, Yng2/YHR090c, and Pho23) and two Schizosaccharomyces pombe proteins (Png1/CAA15917 and Png2/CAA21250) share significant sequence identity with the human candidate tumor suppressor p33(ING1) in their C-terminal regions. The homologous regions contain PHD finger domains which have been implicated in chromatin-mediated transcriptional regulation. We show that GFP-Yng2, like human Ing1, is localized in the nucleus. Deletion of YNG2 results in several phenotypes, including an abnormal multibudded morphology, an inability to utilize nonfermentable carbon sources, heat shock sensitivity, slow growth, temperature sensitivity, and sensitivity to caffeine. These phenotypes are suppressed by expression of either human Ing1 or S. pombe Png1, suggesting that the yeast and human proteins are functionally conserved. Yng1- and Pho23-deficient cells also share some of these phenotypes. We demonstrated by yeast two-hybrid and coimmunoprecipitation tests that Yng2 interacts with Tra1, a component of histone acetyltransferase (HAT) complexes. We further demonstrated by coimmunoprecipitation that HA-Yng1, HA-Yng2, HA-Pho23, and HA-Ing1 are associated with HAT activities in yeast. Genetic and biochemical evidence indicate that the Yng2-associated HAT is Esa1, suggesting that Yng2 is a component of the NuA4 HAT complex. These studies suggest that the yeast Ing1-related proteins are involved in chromatin remodeling. They further suggest that these functions may be conserved in mammals and provide a possible mechanism for the human Ing1 candidate tumor suppressor.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Role of an ING1 growth regulator in transcriptional activation and targeted histone acetylation by the NuA4 complex.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Nov;21(22):7629-40. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.22.7629-7640.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11604499 Free PMC article.
-
Human ING1 proteins differentially regulate histone acetylation.J Biol Chem. 2002 Aug 16;277(33):29832-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M200197200. Epub 2002 May 15. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12015309
-
Opposite role of yeast ING family members in p53-dependent transcriptional activation.J Biol Chem. 2003 May 23;278(21):19171-5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C300036200. Epub 2003 Apr 2. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12672825
-
ING1 and ING2: multifaceted tumor suppressor genes.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Oct;70(20):3753-72. doi: 10.1007/s00018-013-1270-z. Epub 2013 Feb 15. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23412501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of the tumour suppressor p33 ING1b in human neoplasia.J Clin Pathol. 2003 Jul;56(7):491-6. doi: 10.1136/jcp.56.7.491. J Clin Pathol. 2003. PMID: 12835293 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A trithorax-group complex purified from Saccharomyces cerevisiae is required for methylation of histone H3.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Jan 8;99(1):90-4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.221596698. Epub 2001 Dec 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 11752412 Free PMC article.
-
ING2 as a novel mediator of transforming growth factor-beta-dependent responses in epithelial cells.J Biol Chem. 2008 May 9;283(19):13269-79. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M708834200. Epub 2008 Mar 11. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18334480 Free PMC article.
-
Subcellular targeting of p33ING1b by phosphorylation-dependent 14-3-3 binding regulates p21WAF1 expression.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Apr;26(8):2947-54. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.8.2947-2954.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16581770 Free PMC article.
-
HSP70 induction by ING proteins sensitizes cells to tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor-mediated apoptosis.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Dec;26(24):9244-55. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01538-06. Epub 2006 Oct 9. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 17030616 Free PMC article.
-
NuA4 lysine acetyltransferase Esa1 is targeted to coding regions and stimulates transcription elongation with Gcn5.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Dec;29(24):6473-87. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01033-09. Epub 2009 Oct 12. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19822662 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aasland R, Gibson T J, Stewart A F. The PHD finger: implications for chromatin-mediated transcriptional regulation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995;20:56–59. - PubMed
-
- Adams A, Gottschling D E, Kaiser C A, Stearns T. Methods in yeast genetics, 1997 ed. Plainview, N.Y: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1998.
-
- Archer S Y, Hodin R A. Histone acetylation and cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1999;9:171–174. - PubMed
-
- Bannister A J, Kouzarides T. The CBP co-activator is a histone acetyltransferase. Nature. 1996;384:641–643. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
