Rck2 kinase is a substrate for the osmotic stress-activated mitogen-activated protein kinase Hog1
- PMID: 10805732
- PMCID: PMC85729
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.11.3887-3895.2000
Rck2 kinase is a substrate for the osmotic stress-activated mitogen-activated protein kinase Hog1
Abstract
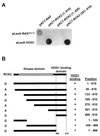
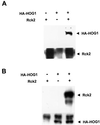
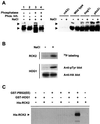
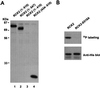
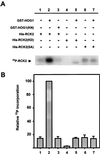
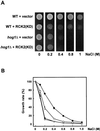
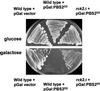
Exposure of yeast cells to increases in extracellular osmolarity activates the Hog1 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). Activation of Hog1 MAPK results in induction of a set of osmoadaptive responses, which allow cells to survive in high-osmolarity environments. Little is known about how the MAPK activation results in induction of these responses, mainly because no direct substrates for Hog1 have been reported. We conducted a two-hybrid screening using Hog1 as a bait to identify substrates for the MAPK, and the Rck2 protein kinase was identified as an interactor for Hog1. Both two-hybrid analyses and coprecipitation assays demonstrated that Hog1 binds strongly to the C-terminal region of Rck2. Upon osmotic stress, Rck2 was phosphorylated in vivo in a Hog1-dependent manner. Furthermore, purified Hog1 was able to phosphorylate Rck2 when activated both in vivo and in vitro. Rck2 phosphorylation occurred specifically at Ser519, a residue located within the C-terminal putative autoinhibitory domain. Interestingly, phosphorylation at Ser519 by Hog1 resulted in an increase of Rck2 kinase activity. Overexpression of Rck2 partially suppressed the osmosensitive phenotype of hog1Delta and pbs2Delta cells, suggesting that Rck2 is acting downstream of Hog1. Consistently, growth arrest caused by hyperactivation of the Hog1 MAPK was abolished by deletion of the RCK2 gene. Furthermore, overexpression of a catalytically impaired (presumably dominant inhibitory) Rck2 kinase resulted in a decrease of osmotolerance in wild-type cells but not in hog1Delta cells. Taken together, our data suggest that Rck2 acts downstream of Hog1, controlling a subset of the responses induced by the MAPK upon osmotic stress.
Figures

References
-
- Albertyn J, Hohmann S, Thevelein J M, Prior B A. GPD1, which encodes glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, is essential for growth under osmotic stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and its expression is regulated by the high-osmolarity glycerol response pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 1994;14:4135–4144. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bartel P L, Chien C, Sternglanz R, Fields S. Using the two-hybrid system to detect protein-protein interactions. In: Hartley D, editor. Cellular interactions in development: a practical approach. Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford University Press; 1993. pp. 153–179.
-
- Boguslawski G. PBS2, a yeast gene encoding a putative protein kinase, interacts with the RAS2 pathway and affects osmotic sensitivity of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Gen Microbiol. 1992;138:2425–2432. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
