(4-aminomethyl)phenylguanidine derivatives as nonpeptidic highly selective inhibitors of human urokinase
- PMID: 10805774
- PMCID: PMC25790
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.10.5113
(4-aminomethyl)phenylguanidine derivatives as nonpeptidic highly selective inhibitors of human urokinase
Abstract
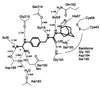
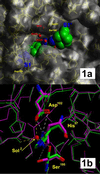
Increased expression of the serine protease urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) in tumor tissues is highly correlated with tumor cell migration, invasion, proliferation, progression, and metastasis. Thus inhibition of uPA activity represents a promising target for antimetastatic therapy. So far, only the x-ray crystal structure of uPA inactivated by H-Glu-Gly-Arg-chloromethylketone has been reported, thus limited data are available for a rational structure-based design of uPA inhibitors. Taking into account the trypsin-like arginine specificity of uPA, (4-aminomethyl)phenylguanidine was selected as a potential P1 residue and iterative derivatization of its amino group with various hydrophobic residues, and structure-activity relationship-based optimization of the spacer in terms of hydrogen bond acceptor/donor properties led to N-(1-adamantyl)-N'-(4-guanidinobenzyl)urea as a highly selective nonpeptidic uPA inhibitor. The x-ray crystal structure of the uPA B-chain complexed with this inhibitor revealed a surprising binding mode consisting of the expected insertion of the phenylguanidine moiety into the S1 pocket, but with the adamantyl residue protruding toward the hydrophobic S1' enzyme subsite, thus exposing the ureido group to hydrogen-bonding interactions. Although in this enzyme-bound state the inhibitor is crossing the active site, interactions with the catalytic residues Ser-195 and His-57 are not observed, but their side chains are spatially displaced for steric reasons. Compared with other trypsin-like serine proteases, the S2 and S3/S4 pockets of uPA are reduced in size because of the 99-insertion loop. Therefore, the peculiar binding mode of the new type of uPA inhibitors offers the possibility of exploiting optimized interactions at the S1'/S2' subsites to further enhance selectivity and potency. Because crystals of the uPA/benzamidine complex allow inhibitor exchange by soaking procedures, the structure-based design of new generations of uPA inhibitors can rely on the assistance of x-ray analysis.
Figures

References
-
- Reuning U, Magdolen V, Wilhelm O, Fischer K, Lutz V, Graeff H, Schmitt M. Int J Oncol. 1998;13:893–906. - PubMed
-
- Schmitt M, Harbeck N, Thomssen C, Wilhelm O, Magdolen V, Reuning U, Ulm K, Höfler H, Jänicke F, Graeff H. Thromb Haemost. 1997;78:285–296. - PubMed
-
- Andreasen P A, Kjøller L, Christensen L, Duffy M J. Int J Cancer. 1997;72:1–22. - PubMed
-
- DeClerck Y A, Imren S, Montgomery A M, Mueller B M, Reisfeld R A, Laug W E. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1997;425:89–97. - PubMed
-
- Ramos-DeSimone N, Hahn-Dantona E, Sipley J, Nagase H, French D L, Quigley J P. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:13066–13076. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

