Tissue factor- and factor X-dependent activation of protease-activated receptor 2 by factor VIIa
- PMID: 10805786
- PMCID: PMC25815
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.10.5255
Tissue factor- and factor X-dependent activation of protease-activated receptor 2 by factor VIIa
Abstract
Protease-activated receptor 2 (PAR2) is expressed by vascular endothelial cells and other cells in which its function and physiological activator(s) are unknown. Unlike PAR1, PAR3, and PAR4, PAR2 is not activatable by thrombin. Coagulation factors VIIa (FVIIa) and Xa (FXa) are proteases that act upstream of thrombin in the coagulation cascade and require cofactors to interact with their substrates. These proteases elicit cellular responses, but their receptor(s) have not been identified. We asked whether FVIIa and FXa might activate PARs if presented by their cofactors. Co-expression of tissue factor (TF), the cellular cofactor for FVIIa, together with PAR1, PAR2, PAR3, or PAR4 conferred TF-dependent FVIIa activation of PAR2 and, to lesser degree, PAR1. Responses to FXa were also observed but were independent of exogenous cofactor. The TF/FVIIa complex converts the inactive zymogen Factor X (FX) to FXa. Strikingly, when FX was present, low picomolar concentrations of FVIIa caused robust signaling in cells expressing TF and PAR2. Responses in keratinocytes and cytokine-treated endothelial cells suggested that PAR2 may be activated directly by TF/FVIIa and indirectly by TF/FVIIa-generated FXa at naturally occurring expression levels of TF and PAR2. These results suggest that PAR2, although not activatable by thrombin, may nonetheless function as a sensor for coagulation proteases and contribute to endothelial activation in the setting of injury and inflammation. More generally, these findings highlight the potential importance of cofactors in regulating PAR function and specificity.
Figures
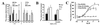

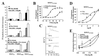

References
-
- Molino M, Barnathan E S, Numerof R, Clark J, Dreyer M, Cumashi A, Hoxie J A, Schechter N, Woolkalis M, Brass L F. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:4043–4049. - PubMed
-
- Ishihara H, Connolly A J, Zeng D, Kahn M L, Zheng Y W, Timmons C, Tram T, Coughlin S R. Nature (London) 1997;386:502–506. - PubMed
-
- Kahn M L, Zheng Y W, Huang W, Bigornia V, Zeng D, Moff S, Farese R V, Jr, Tam C, Coughlin S R. Nature (London) 1998;394:690–694. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

