Novel gene conversion between X-Y homologues located in the nonrecombining region of the Y chromosome in Felidae (Mammalia)
- PMID: 10805789
- PMCID: PMC25824
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.10.5307
Novel gene conversion between X-Y homologues located in the nonrecombining region of the Y chromosome in Felidae (Mammalia)
Abstract
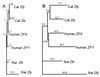
Genes located on the mammalian Y chromosome outside of the pseudoautosomal region do not recombine with those on the X and are predicted to either undergo selection for male function or gradually degenerate because of an accumulation of deleterious mutations. Here, phylogenetic analyses of X-Y homologues, Zfx and Zfy, among 26 felid species indicate two ancestral episodes of directed genetic exchange (ectopic gene conversion) from X to Y: once during the evolution of pallas cat and once in a common predecessor of ocelot lineage species. Replacement of the more rapidly evolving Y homologue with the evolutionarily constrained X copy may represent a mechanism for adaptive editing of functional genes on the nonrecombining region of the mammalian Y chromosome.
Figures


References
-
- Ellison J W, Li X, Francke U, Shapiro L J. Mamm Genome. 1996;7:25–30. - PubMed
-
- Lahn B, Page D. Science. 1999;286:964–967. - PubMed
-
- Graves J A M. BioEssays. 1995;17:311–321. - PubMed
-
- Graves J A M. J Exp Zool. 1998;281:472–481. - PubMed
-
- Charlesworth B, Charlesworth D. Genet Res. 1997;70:63–73. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

