Ultrasensitive detection of pathological prion protein aggregates by dual-color scanning for intensely fluorescent targets
- PMID: 10805803
- PMCID: PMC25852
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.10.5468
Ultrasensitive detection of pathological prion protein aggregates by dual-color scanning for intensely fluorescent targets
Abstract
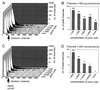
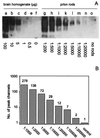
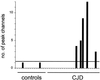
A definite diagnosis of prion diseases such as Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) relies on the detection of pathological prion protein (PrP(Sc)). However, no test for PrP(Sc) in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) has been available thus far. Based on a setup for confocal dual-color fluorescence correlation spectroscopy, a technique suitable for single molecule detection, we developed a highly sensitive detection method for PrP(Sc). Pathological prion protein aggregates were labeled by specific antibody probes tagged with fluorescent dyes, resulting in intensely fluorescent targets, which were measured by dual-color fluorescence intensity distribution analysis in a confocal scanning setup. In a diagnostic model system, PrP(Sc) aggregates were detected down to a concentration of 2 pM PrP(Sc), corresponding to an aggregate concentration of approximately 2 fM, which was more than one order of magnitude more sensitive than Western blot analysis. A PrP(Sc)-specific signal could also be detected in a number of CSF samples from patients with CJD but not in control samples, providing the basis for a rapid and specific test for CJD and other prion diseases. Furthermore, this method could be adapted to the sensitive detection of other disease-associated amyloid aggregates such as in Alzheimer's disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Putting prions into focus: application of single molecule detection to the diagnosis of prion diseases.Arch Virol Suppl. 2000;(16):161-71. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-6308-5_15. Arch Virol Suppl. 2000. PMID: 11214919
-
Ultrasensitive human prion detection in cerebrospinal fluid by real-time quaking-induced conversion.Nat Med. 2011 Feb;17(2):175-8. doi: 10.1038/nm.2294. Epub 2011 Jan 30. Nat Med. 2011. PMID: 21278748
-
RT-QuIC: a new test for sporadic CJD.Pract Neurol. 2019 Feb;19(1):49-55. doi: 10.1136/practneurol-2018-001935. Epub 2018 Oct 3. Pract Neurol. 2019. PMID: 30282760 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular biology of prions causing infectious and genetic encephalopathies of humans as well as scrapie of sheep and BSE of cattle.Dev Biol Stand. 1991;75:55-74. Dev Biol Stand. 1991. PMID: 1686599 Review.
-
Synaptic pathology and cell death in the cerebellum in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease.Cerebellum. 2002 Jul;1(3):213-22. doi: 10.1080/14734220260418448. Cerebellum. 2002. PMID: 12879983 Review.
Cited by
-
A New Approach for Detection Improvement of the Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disorder through a Specific Surface Chemistry Applied onto Titration Well.Biosensors (Basel). 2012 Oct 24;2(4):433-47. doi: 10.3390/bios2040433. Biosensors (Basel). 2012. PMID: 25586034 Free PMC article.
-
Ensuring the biologic safety of plasma-derived therapeutic proteins: detection, inactivation, and removal of pathogens.BioDrugs. 2005;19(2):79-96. doi: 10.2165/00063030-200519020-00002. BioDrugs. 2005. PMID: 15807628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel fluorescence labeling and high-throughput assay technologies for in vitro analysis of protein interactions.Genome Res. 2002 Mar;12(3):487-92. doi: 10.1101/gr.218802. Genome Res. 2002. PMID: 11875038 Free PMC article.
-
There and back again: from the origin of life to single molecules.Eur Biophys J. 2018 May;47(4):493-498. doi: 10.1007/s00249-018-1295-1. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Eur Biophys J. 2018. PMID: 29569181 Free PMC article.
-
Filtered FCS: species auto- and cross-correlation functions highlight binding and dynamics in biomolecules.Chemphyschem. 2012 Mar;13(4):1036-53. doi: 10.1002/cphc.201100897. Epub 2012 Mar 7. Chemphyschem. 2012. PMID: 22407544 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

