Potent and nontoxic antisense oligonucleotides containing locked nucleic acids
- PMID: 10805816
- PMCID: PMC25880
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.10.5633
Potent and nontoxic antisense oligonucleotides containing locked nucleic acids
Abstract
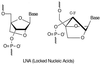
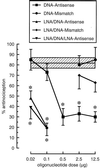
Insufficient efficacy and/or specificity of antisense oligonucleotides limit their in vivo usefulness. We demonstrate here that a high-affinity DNA analog, locked nucleic acid (LNA), confers several desired properties to antisense agents. Unlike DNA, LNA/DNA copolymers were not degraded readily in blood serum and cell extracts. However, like DNA, the LNA/DNA copolymers were capable of activating RNase H, an important antisense mechanism of action. In contrast to phosphorothioate-containing oligonucleotides, isosequential LNA analogs did not cause detectable toxic reactions in rat brain. LNA/DNA copolymers exhibited potent antisense activity on assay systems as disparate as a G-protein-coupled receptor in living rat brain and an Escherichia coli reporter gene. LNA-containing oligonucleotides will likely be useful for many antisense applications.
Figures


References
-
- Wahlestedt C, Good L. Curr Opin Drug Disc Dev. 1999;2:142–146. - PubMed
-
- Stein C A. Nat Biotechnol. 1999;17:209. - PubMed
-
- Branch A D. Trends Biochem Sci. 1998;23:45–50. - PubMed
-
- Crooke S T. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev. 1998;8:vii–viii. - PubMed
-
- Perry C M, Balfour J A. Drugs. 1999;57:375–380. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

