Mutation of Arabidopsis plastid phosphoglucose isomerase affects leaf starch synthesis and floral initiation
- PMID: 10806248
- PMCID: PMC59005
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.123.1.319
Mutation of Arabidopsis plastid phosphoglucose isomerase affects leaf starch synthesis and floral initiation
Abstract
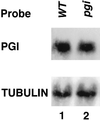
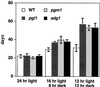
We isolated pgi1-1, an Arabidopsis mutant with a decreased plastid phospho-glucose (Glc) isomerase activity. While pgi1-1 mutant has a deficiency in leaf starch synthesis, it accumulates starch in root cap cells. It has been shown that a plastid transporter for hexose phosphate transports cytosolic Glc-6-P into plastids and expresses restricted mainly to the heterotrophic tissues. The decreased starch content in leaves of the pgi1-1 mutant indicates that cytosolic Glc-6-P cannot be efficiently transported into chloroplasts to complement the mutant's deficiency in chloroplastic phospho-Glc isomerase activity for starch synthesis. We cloned the Arabidopsis PGI1 gene and showed that it encodes the plastid phospho-Glc isomerase. The pgi1-1 allele was found to have a single nucleotide substitution, causing a Ser to Phe transition. While the flowering times of the Arabidopsis starch-deficient mutants pgi1, pgm1, and adg1 were similar to that of the wild type under long-day conditions, it was significantly delayed under short-day conditions. The pleiotropic phenotype of late flowering conferred by these starch metabolic mutations suggests that carbohydrate metabolism plays an important role in floral initiation.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The role of plastidial glucose-6-phosphate/phosphate translocators in vegetative tissues of Arabidopsis thaliana mutants impaired in starch biosynthesis.Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2010 Sep;12 Suppl 1:115-28. doi: 10.1111/j.1438-8677.2010.00349.x. Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2010. PMID: 20712627
-
Plastidic phosphoglucose isomerase is an important determinant of starch accumulation in mesophyll cells, growth, photosynthetic capacity, and biosynthesis of plastidic cytokinins in Arabidopsis.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 26;10(3):e0119641. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119641. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25811607 Free PMC article.
-
Defects in leaf carbohydrate metabolism compromise acclimation to high light and lead to a high chlorophyll fluorescence phenotype in Arabidopsis thaliana.BMC Plant Biol. 2012 Jan 16;12:8. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-12-8. BMC Plant Biol. 2012. PMID: 22248311 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis Responds to Alternaria alternata Volatiles by Triggering Plastid Phosphoglucose Isomerase-Independent Mechanisms.Plant Physiol. 2016 Nov;172(3):1989-2001. doi: 10.1104/pp.16.00945. Epub 2016 Sep 23. Plant Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27663407 Free PMC article.
-
Plastidial Phosphoglucose Isomerase Is an Important Determinant of Seed Yield through Its Involvement in Gibberellin-Mediated Reproductive Development and Storage Reserve Biosynthesis in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2018 Sep;30(9):2082-2098. doi: 10.1105/tpc.18.00312. Epub 2018 Aug 10. Plant Cell. 2018. PMID: 30099384 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cytosolic phosphoglucose isomerase is essential for microsporogenesis and embryogenesis in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol. 2023 Jan 2;191(1):177-198. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiac494. Plant Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36271861 Free PMC article.
-
A structural basis for the functional differences between the cytosolic and plastid phosphoglucose isomerase isozymes.PLoS One. 2022 Sep 1;17(9):e0272647. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0272647. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36048814 Free PMC article.
-
Increasing growth and yield by altering carbon metabolism in a transgenic leaf oil crop.Plant Biotechnol J. 2020 Oct;18(10):2042-2052. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13363. Epub 2020 Mar 18. Plant Biotechnol J. 2020. PMID: 32069385 Free PMC article.
-
Starch biosynthetic genes and enzymes are expressed and active in the absence of starch accumulation in sugar beet tap-root.BMC Plant Biol. 2014 Apr 23;14:104. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-14-104. BMC Plant Biol. 2014. PMID: 24758347 Free PMC article.
-
Rethinking Guard Cell Metabolism.Plant Physiol. 2016 Nov;172(3):1371-1392. doi: 10.1104/pp.16.00767. Epub 2016 Sep 8. Plant Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27609861 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Borchert S, Grosse H, Heldt HW. Specific transport of inorganic phosphate, glucose 6-phosphate, dihydroxyacetone phosphate and 3-phosphoglycerate into amyloplasts from pea roots. FEBS Lett. 1989;253:183–186.
-
- Caspar T. Genetic dissection of the biosynthesis, degradation, and biological functions of starch. In: Meyerowitz EM, Somerville CR, editors. Arabidopsis. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1994. pp. 913–936.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

