Comparison of serum, cerebrospinal fluid and brain extracellular fluid pharmacokinetics of lamotrigine
- PMID: 10807660
- PMCID: PMC1572088
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703337
Comparison of serum, cerebrospinal fluid and brain extracellular fluid pharmacokinetics of lamotrigine
Abstract
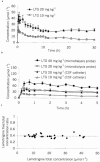
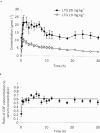
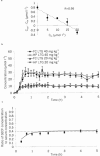
We investigated the rate of penetration into and the intra-relationship between the serum, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and regional brain extracellular fluid (bECF) compartments following systemic administration of lamotrigine in rat. The serum pharmacokinetics were biphasic with an initial distribution phase, (half-life approximately 3 h), and then a prolonged elimination phase of over 30 h. The serum pharmacokinetics were linear over the range 10 - 40 mg kg(-1). Using direct sampling of CSF with concomitant serum sampling, the calculated penetration half-time into CSF was 0.42+/-0.15 h. At equilibrium, the CSF to total serum concentration ratio (0.61+/-0.02) was greater than the free to total serum concentration (0.39+/-0.01). Using in vivo recovery corrected microdialysis sampling in frontal cortex and hippocampus with concomitant serum sampling, the calculated penetration half-time of lamotrigine into bECF, 0.51+/-0.11 h, was similar to that for CSF and was not area or dose dependent. At equilibrium, the bECF to total serum concentration ratio (0.40+/-0.04) was similar to the free to total serum concentration (0.39+/-0.01), and did not differ between hippocampus and frontal cortex. The species specific serum kinetics can explain the prolonged action of lamotrigine in rat seizure models. Lamotrigine has a relatively slow penetration into both CSF and bECF compartments compared with antiepileptic drugs used in acute seizures. Furthermore, the free serum drug concentration is not the sole contributor to the CSF compartment, and the CSF concentration is an overestimate of the bECF concentration of lamotrigine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The pharmacokinetic inter-relationship of tiagabine in blood, cerebrospinal fluid and brain extracellular fluid (frontal cortex and hippocampus).Seizure. 2004 Dec;13(8):574-81. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2004.01.007. Seizure. 2004. PMID: 15519917
-
The pharmacokinetics of vigabatrin in rat blood and cerebrospinal fluid.Seizure. 2007 Jan;16(1):43-9. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2006.10.003. Epub 2006 Nov 22. Seizure. 2007. PMID: 17118677
-
Comparison of brain extracellular fluid, brain tissue, cerebrospinal fluid, and serum concentrations of antiepileptic drugs measured intraoperatively in patients with intractable epilepsy.Epilepsia. 2006 Apr;47(4):681-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2006.00504.x. Epilepsia. 2006. PMID: 16650134
-
The use of microdialysis in CNS drug delivery studies. Pharmacokinetic perspectives and results with analgesics and antiepileptics.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2000 Dec 15;45(2-3):283-94. doi: 10.1016/s0169-409x(00)00109-5. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2000. PMID: 11108980 Review.
-
Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling to investigate regional brain distribution kinetics in rats.AAPS J. 2012 Sep;14(3):543-53. doi: 10.1208/s12248-012-9366-1. Epub 2012 May 17. AAPS J. 2012. PMID: 22588644 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Time course of the effects of the serotonin-selective reuptake inhibitor sertraline on central and peripheral serotonin neurochemistry in the rhesus monkey.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005 Mar;178(2-3):339-46. doi: 10.1007/s00213-004-2011-7. Epub 2004 Sep 25. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005. PMID: 15452685
-
Considerations in the use of cerebrospinal fluid pharmacokinetics to predict brain target concentrations in the clinical setting: implications of the barriers between blood and brain.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2002;41(10):691-703. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200241100-00001. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2002. PMID: 12162757 Review.
-
Neonatal exposure to antiepileptic drugs disrupts striatal synaptic development.Ann Neurol. 2012 Sep;72(3):363-72. doi: 10.1002/ana.23600. Epub 2012 May 11. Ann Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22581672 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of CSF in translational neuroscience.J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2013 Jun;40(3):315-26. doi: 10.1007/s10928-013-9301-9. Epub 2013 Feb 12. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2013. PMID: 23400635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulatory effects of neuropsychopharmaca on intracellular pH of hippocampal neurones in vitro.Br J Pharmacol. 2010 Jan 1;159(2):474-83. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00540.x. Epub 2009 Dec 10. Br J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20015293 Free PMC article.
References
-
- BAUDRIE V., ROULLET J.B., GOUREAU Y., CHAOULOFF F., ELGHOZI J.L. Determination of cerebrospinal fluid production rate using a push-pull perfusion procedure in the conscious rat. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 1990;4:269–274. - PubMed
-
- CORNFORD E.M., YOUNG D., PAXTON J.W., SOFIA R.D. Blood-brain barrier penetration of felbamate. Epilepsia. 1992;33:944–954. - PubMed
-
- CRUMRINE R.C., BERGSTRAND K., COOPER A.T., FAISON W.L., COOPER B.R. Lamotrigine protects hippocampal CA1 neurons from ischemic damage after cardiac arrest. Stroke. 1997;28:2230–2236. - PubMed
-
- DAVSON H., SEGAL M.B. Physiology of the CSF and blood brain barriers. Florida: CRC Press; 1995.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

