Modulation of (3)H-noradrenaline release by presynaptic opioid, cannabinoid and bradykinin receptors and beta-adrenoceptors in mouse tissues
- PMID: 10807669
- PMCID: PMC1572066
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703305
Modulation of (3)H-noradrenaline release by presynaptic opioid, cannabinoid and bradykinin receptors and beta-adrenoceptors in mouse tissues
Abstract
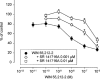
Release-modulating opioid and cannabinoid (CB) receptors, beta-adrenoceptors and bradykinin receptors at noradrenergic axons were studied in mouse tissues (occipito-parietal cortex, heart atria, vas deferens and spleen) preincubated with (3)H-noradrenaline. Experiments using the OP(1) receptor-selective agonists DPDPE and DSLET, the OP(2)-selective agonists U50488H and U69593, the OP(3)-selective agonist DAMGO, the ORL(1) receptor-selective agonist nociceptin, and a number of selective antagonists showed that the noradrenergic axons innervating the occipito-parietal cortex possess release-inhibiting OP(3) and ORL(1) receptors, those innervating atria OP(1), ORL(1) and possibly OP(3) receptors, and those innervating the vas deferens all four opioid receptor types. Experiments using the non-selective CB agonists WIN 55,212-2 and CP 55,940 and the CB(1)-selective antagonist SR 141716A indicated that the noradrenergic axons of the vas deferens possess release-inhibiting CB(1) receptors. Presynaptic CB receptors were not found in the occipito-parietal cortex, in atria or in the spleen. Experiments using the non-selective beta-adrenoceptor agonist isoprenaline and the beta(2)-selective agonist salbutamol, as well as subtype-selective antagonists, demonstrated the occurrence of release-enhancing beta(2)-adrenoceptors at the sympathetic axons of atria and the spleen, but demonstrated their absence in the occipito-parietal cortex and the vas deferens. Experiments with bradykinin and the B(2)-selective antagonist Hoe 140 showed the operation of release-enhancing B(2) receptors at the sympathetic axons of atria, the vas deferens and the spleen, but showed their absence in the occipito-parietal cortex. The experiments document a number of new presynaptic receptor locations. They confirm and extend the existence of marked tissue and species differences in presynaptic receptors at noradrenergic neurons.
Figures
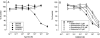
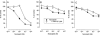
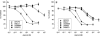

Similar articles
-
Postnatal development of presynaptic receptors that modulate noradrenaline release in mice.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2001 Oct;364(4):359-71. doi: 10.1007/s002100100455. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11683524
-
Distinct mixtures of muscarinic receptor subtypes mediate inhibition of noradrenaline release in different mouse peripheral tissues, as studied with receptor knockout mice.Br J Pharmacol. 2005 Aug;145(8):1153-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706297. Br J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15965496 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for presynaptic cannabinoid CB(1) receptor-mediated inhibition of noradrenaline release in the guinea pig lung.Eur J Pharmacol. 2001 Nov 16;431(2):237-44. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(01)01413-3. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11728431
-
Modulation of noradrenaline release by activation of presynaptic beta-adrenoceptors in the cardiovascular system.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;604:528-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb32018.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990. PMID: 1977360 Review.
-
Subtype classification of presynaptic alpha 2-adrenoceptors.Gen Pharmacol. 1993 Jan;24(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(93)90003-g. Gen Pharmacol. 1993. PMID: 8387042 Review.
Cited by
-
Urethane, but not pentobarbitone, attenuates presynaptic receptor function in rats: a contribution to the choice of anaesthetic.Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Aug;157(8):1474-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00315.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19681871 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabinoid CB1 receptor activation, pharmacological blockade, or genetic ablation affects the function of the muscarinic auto- and heteroreceptor.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2012 Apr;385(4):385-96. doi: 10.1007/s00210-011-0717-8. Epub 2012 Jan 4. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22215206
-
Physiological and pharmacological aspects of the vas deferens-an update.Front Pharmacol. 2013 Aug 22;4:101. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2013.00101. eCollection 2013. Front Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23986701 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between presynaptic angiotensin receptors, bradykinin receptors and alpha 2-autoreceptors in sympathetic neurons: a study in alpha 2-adrenoceptor-deficient mice.Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Apr;138(8):1389-402. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705223. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12721093 Free PMC article.
-
Presynaptic Adrenoceptors.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2024;285:185-245. doi: 10.1007/164_2024_714. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38755350 Review.
References
-
- ALTMAN J.D., TRENDELENBURG A.U., MACMILLAN L., BERNSTEIN D., LIMBIRD L., STARKE K., KOBILKA B.K., HEIN L. Abnormal regulation of the sympathetic nervous system in α2A-adrenergic receptor knockout mice. Mol. Pharmacol. 1999;56:154–161. - PubMed
-
- BERZETEI-GURSKE I.P., SCHWARTZ R.W., TOLL L. Determination of activity for nociceptin in the mouse vas deferens. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1996;302:R1–R2. - PubMed
-
- BILSKI A.J., HALLIDAY S.E., FITZGERALD J.D., WALE J.L. The pharmacology of a β2-selective adrenoceptor antagonist (ICI 118,551) J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1983;5:430–437. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

