Troglitazone prevents and reverses dexamethasone induced insulin resistance on glycogen synthesis in 3T3 adipocytes
- PMID: 10807673
- PMCID: PMC1572073
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703313
Troglitazone prevents and reverses dexamethasone induced insulin resistance on glycogen synthesis in 3T3 adipocytes
Abstract
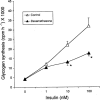
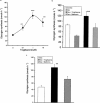
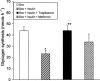
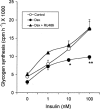
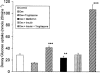
Troglitazone lowers blood glucose levels in Type II diabetic patients. To evaluate the insulin sensitizing action of troglitazone on glycogen synthesis we have used dexamethasone-treated 3T3 adipocytes as an in vitro model. Differentiated 3T3 adipocytes were incubated with 100 nM dexamethasone for 6 days. Troglitazone (1.0 microM) or metformin (1.0 mM) with or without 200 nM insulin was added during the last 4 days. At the end, insulin (100 nM) stimulated glycogen synthesis was determined using (14)C-glucose. Dexamethasone caused a 50% reduction in glycogen synthesis. Troglitazone caused an approximately 3 fold increase in glycogen synthesis from 43.9+/-3.4 to 120+/-16.2 nmols h(-1). Under identical conditions metformin had no significant effect. When cells were incubated with troglitazone and dexamethasone simultaneously for 6 days, troglitazone but not metformin completely prevented dexamethasone-induced insulin resistance. RU 486 (1.0 microM) also completely prevented the insulin resistance. Chronic incubation with dexamethasone and insulin resulted in a 73% reduction in glycogen synthesis. In these adipocytes, troglitazone was partially active with glycogen synthesis rising from 23.1+/-3.0 to 44.4+/-4.5 nmol h(-1), P<0.01 while metformin was inactive. Troglitazone stimulated 2-deoxyglucose uptake by 2 - 3 fold in dexamethasone-treated adipocytes. Metformin also increased glucose uptake significantly. Troglitazone did not affect insulin binding while a 2 fold increase was observed in normal adipocytes where it exhibited a modest effect. Since the effect of troglitazone was greater in dexamethasone-treated adipocytes, troglitazone is likely to act by preventing dexamethasone-induced alterations which may include (i) binding to glucocorticoid receptor and (ii) effect on glucose uptake. These data demonstrate the direct insulin sensitizing action of troglitazone on glycogen synthesis and suggest a pharmacological profile different from metformin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of vanadate on glycogen synthesis in dexamethasone-treated 3T3 adipocytes: evidence for a novel insulin sensitizing action.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2001 Aug;3(4):271-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1463-1326.2001.00130.x. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2001. PMID: 11520307
-
Troglitazone enhances differentiation, basal glucose uptake, and Glut1 protein levels in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.Endocrinology. 1996 Nov;137(11):4706-12. doi: 10.1210/endo.137.11.8895337. Endocrinology. 1996. PMID: 8895337
-
Troglitazone antagonizes metabolic effects of glucocorticoids in humans: effects on glucose tolerance, insulin sensitivity, suppression of free fatty acids, and leptin.Diabetes. 2002 Oct;51(10):2895-902. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.51.10.2895. Diabetes. 2002. PMID: 12351424 Clinical Trial.
-
[Troglitazone].Nihon Rinsho. 2000 Feb;58(2):389-94. Nihon Rinsho. 2000. PMID: 10707563 Review. Japanese.
-
Troglitazone. Is it all over?Neth J Med. 1999 Jul;55(1):4-12. doi: 10.1016/s0300-2977(99)00021-2. Neth J Med. 1999. PMID: 10431549 Review.
Cited by
-
GLP-1 receptor agonist promotes brown remodelling in mouse white adipose tissue through SIRT1.Diabetologia. 2016 May;59(5):1059-69. doi: 10.1007/s00125-016-3896-5. Epub 2016 Feb 29. Diabetologia. 2016. PMID: 26924394
-
Polyphenol Stilbenes from Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) Seeds Improve Insulin Sensitivity and Mitochondrial Function in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Jun 5;2018:7634362. doi: 10.1155/2018/7634362. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 29967664 Free PMC article.
-
AICAR positively regulate glycogen synthase activity and LDL receptor expression through Raf-1/MEK/p42/44MAPK/p90RSK/GSK-3 signaling cascade.Biochem Pharmacol. 2008 Jan 15;75(2):457-67. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2007.08.028. Epub 2007 Sep 1. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 17945190 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of p1736, a novel antidiabetic compound that improves peripheral insulin sensitivity in mice models.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 23;8(10):e77946. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077946. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24194903 Free PMC article.
References
-
- BAILEY C.J. Biguanides and NIDDM. Diabetes Care. 1992;15:755–772. - PubMed
-
- CIARALDI T.P., GILMORE A., OLEFSKY J.M., GOLDBER G.M., HEIDENREICH K.A. In vitro studies on the action of CS-045. A new antidiabetic agent. Metabolism. 1990;39:1056–1062. - PubMed
-
- DAMSBO P., HERMANN L.S., VAAG A., HOTHER-NEILSEN O., BECK-NEILSEN H. Irreversibility of the defect in glycogen synthase activity in skeletal muscle from obese patients with NIDDM treated with diet and metformin. Diabetes Care. 1998;21:1489–1494. - PubMed
-
- DAMSBO P., VAAG A., HOTHER-NIELSEN O., BECK-NEILSEN H. Reduced glycogen synthase activity in skeletal muscle from obese patients with and without type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1991;34:239–245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

