Use of (99m)Tc-DISIDA biliary scanning with morphine provocation for the detection of elevated sphincter of Oddi basal pressure
- PMID: 10807897
- PMCID: PMC1756444
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.46.6.838
Use of (99m)Tc-DISIDA biliary scanning with morphine provocation for the detection of elevated sphincter of Oddi basal pressure
Abstract
Background: Endoscopic biliary manometry is useful in the assessment of patients with types II and III sphincter of Oddi dysfunction, but it is time consuming and invasive.
Aim: To investigate the role of (99m)Tc-DISIDA scanning, with and without morphine provocation, as a non-invasive investigation in these patients compared with endoscopic biliary manometry.
Subjects and methods: A total of 34 patients with a clinical diagnosis of type II (n = 21) or III (n = 13) sphincter of Oddi dysfunction were studied. Biliary scintigraphy with 100 MBq of (99m)Tc-DISIDA was carried out with and without morphine provocation (0.04 mg/kg intravenously) and time/activity curves were compared with the results of subsequent endoscopic biliary manometry.
Results: Eighteen (nine type II, nine type III) of the 34 (53%) patients had sphincter of Oddi basal pressures above the upper limit of normal (40 mm Hg). In the standard DISIDA scan without morphine, no significant differences were observed in time to maximal activity (Tmax) or percentage excretion at 45 or 60 minutes between those with normal and those with abnormal biliary manometry. However, following morphine provocation, median percentage excretion at 60 minutes was 4.9% in those with abnormal manometry and 28.2% in the normal manometry group (p = 0.002). Using a cut off value of 15% excretion at 60 minutes, the sensitivity for detecting elevated sphincter of Oddi basal pressure by the morphine augmented DISIDA scan was 83% and specificity was 81%. Also, 14 of the 18 patients with abnormal manometry complained of biliary-type pain after morphine infusion compared with only two of 16 patients in the normal manometry group (p = 0.001).
Conclusions: (99m)Tc-DISIDA with morphine provocation is a useful non-invasive investigation for types II and III sphincter of Oddi dysfunction to detect those with elevated sphincter basal pressures who may respond to endoscopic sphincterotomy.
Figures
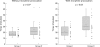
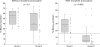
Comment in
-
Morphine and biliary pain revisited.Gut. 2000 Jun;46(6):750-1. doi: 10.1136/gut.46.6.750. Gut. 2000. PMID: 10807881 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Quantitative 99mTc-DISIDA scanning and endoscopic biliary manometry in sphincter of Oddi dysfunction.Gut. 1988 Oct;29(10):1397-401. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.10.1397. Gut. 1988. PMID: 3197984 Free PMC article.
-
Outcome of endoscopic sphincterotomy in post cholecystectomy patients with sphincter of Oddi dysfunction as predicted by manometry and quantitative choledochoscintigraphy.Gut. 2002 May;50(5):665-8. doi: 10.1136/gut.50.5.665. Gut. 2002. PMID: 11950813 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term clinical outcome of post-cholecystectomy patients with biliary-type pain: results of manometry, non-invasive techniques and endoscopic sphincterotomy.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1996 Mar;8(3):245-9. doi: 10.1097/00042737-199603000-00011. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1996. PMID: 8724025
-
Evaluation of sphincter of Oddi function.Aust N Z J Surg. 1989 Jun;59(6):445-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-2197.1989.tb01608.x. Aust N Z J Surg. 1989. PMID: 2660779 Review.
-
Efficacy of biliary scintigraphy in suspected sphincter of Oddi dysfunction.Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2001 Apr;3(2):160-5. doi: 10.1007/s11894-001-0014-7. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2001. PMID: 11276385 Review.
Cited by
-
Sphincter of Oddi disorder: what is the clinical issue?Clin J Gastroenterol. 2011 Dec;4(6):364-70. doi: 10.1007/s12328-011-0260-7. Epub 2011 Oct 27. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 26189737
-
Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction: managing the patient with chronic biliary pain.World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Jun 28;12(24):3793-802. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i24.3793. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 16804961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Scintigraphy versus manometry in patients with suspected biliary sphincter of Oddi dysfunction.Gut. 2003 Mar;52(3):352-7. doi: 10.1136/gut.52.3.352. Gut. 2003. PMID: 12584215 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic sphincterotomy: technique, indications, and complications.World J Gastroenterol. 2007 Aug 14;13(30):4064-71. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i30.4064. World J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17696223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The sphincter of oddi.Dig Dis Sci. 2007 May;52(5):1211-8. doi: 10.1007/s10620-006-9171-8. Epub 2007 Mar 14. Dig Dis Sci. 2007. PMID: 17356921 Review. No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
