Morphogenesis, adhesive properties, and antifungal resistance depend on the Pmt6 protein mannosyltransferase in the fungal pathogen candida albicans
- PMID: 10809683
- PMCID: PMC94490
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.182.11.3063-3071.2000
Morphogenesis, adhesive properties, and antifungal resistance depend on the Pmt6 protein mannosyltransferase in the fungal pathogen candida albicans
Abstract
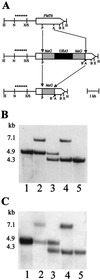
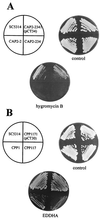
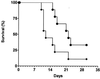
Protein mannosyltransferases (Pmt proteins) initiate O glycosylation of secreted proteins in fungi. We have characterized PMT6, which encodes the second Pmt protein of the fungal pathogen Candida albicans. The residues of Pmt6p are 21 and 42% identical to those of C. albicans Pmt1p and S. cerevisiae Pmt6p, respectively. Mutants lacking one or two PMT6 alleles grow normally and contain normal Pmt enzymatic activities in cell extracts but show phenotypes including a partial block of hyphal formation (dimorphism) and a supersensitivity to hygromycin B. The morphogenetic defect can be suppressed by overproduction of known components of signaling pathways, including Cek1p, Cph1p, Tpk2p, and Efg1p, suggesting a specific Pmt6p target protein upstream of these components. Mutants lacking both PMT1 and PMT6 are viable and show pmt1 mutant phenotypes and an additional sensitivity to the iron chelator ethylenediamine-di(o-hydroxyphenylacetic acid). The lack of Pmt6p significantly reduces adherence to endothelial cells and overall virulence in a mouse model of systemic infection. The results suggest that Pmt6p regulates a more narrow subclass of proteins in C. albicans than Pmt1p, including secreted proteins responsible for morphogenesis and antifungal sensitivities.
Figures


Similar articles
-
PMT family of Candida albicans: five protein mannosyltransferase isoforms affect growth, morphogenesis and antifungal resistance.Mol Microbiol. 2005 Jan;55(2):546-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04401.x. Mol Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15659169
-
Multiple functions of Pmt1p-mediated protein O-mannosylation in the fungal pathogen Candida albicans.J Biol Chem. 1998 Aug 14;273(33):20837-46. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.33.20837. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9694829
-
O-glycosylation.Med Mycol. 2001;39 Suppl 1:67-74. Med Mycol. 2001. PMID: 11800270 Review.
-
Virulence of the fungal pathogen Candida albicans requires the five isoforms of protein mannosyltransferases.Infect Immun. 2005 Aug;73(8):4571-80. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.8.4571-4580.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 16040968 Free PMC article.
-
Fungal Mannosyltransferases as Fitness Attributes and their Contribution to Virulence.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2017;18(11):1065-1073. doi: 10.2174/1389203717666160813164253. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2017. PMID: 27526929 Review.
Cited by
-
Posttranslational modifications of proteins in the pathobiology of medically relevant fungi.Eukaryot Cell. 2012 Feb;11(2):98-108. doi: 10.1128/EC.05238-11. Epub 2011 Dec 9. Eukaryot Cell. 2012. PMID: 22158711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biochemical characterization of recombinant Candida albicans mannosyltransferases Mnt1, Mnt2 and Mnt5 reveals new functions in O- and N-mannan biosynthesis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012 Mar 2;419(1):77-82. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.01.131. Epub 2012 Feb 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012. PMID: 22326920 Free PMC article.
-
Linking Cellular Morphogenesis with Antifungal Treatment and Susceptibility in Candida Pathogens.J Fungi (Basel). 2019 Feb 21;5(1):17. doi: 10.3390/jof5010017. J Fungi (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30795580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of O-mannosylated virulence factors in Ustilago maydis.PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(3):e1002563. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002563. Epub 2012 Mar 1. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 22416226 Free PMC article.
-
The Fusarium oxysporum gnt2, encoding a putative N-acetylglucosamine transferase, is involved in cell wall architecture and virulence.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 27;8(12):e84690. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084690. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24416097 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aramayo R, Metzenberg R L. Meiotic transvection in fungi. Cell. 1996;86:103–113. - PubMed
-
- Bourdineaud J-P, van der Vaart J M, Donzeau M, de Sampaio G, Verrips C T, Lauquin G J-M. Pmt1 mannosyltransferase is involved in cell wall incorporation of several proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Microbiol. 1998;27:85–98. - PubMed
-
- Cannon R D, Jenkinson H F, Shepherd M G. Cloning and expression of Candida albicans ADE2 and proteinase genes on a replicative plasmid in C. albicans and in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1992;235:453–457. - PubMed
-
- Cassone A, Sullivan P A, Shepherd M G. N-acetyl-D-glucosamine-induced morphogenesis in Candida albicans. Microbiologica. 1985;8:85–99. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

