Evidence that SpoIVFB is a novel type of membrane metalloprotease governing intercompartmental communication during Bacillus subtilis sporulation
- PMID: 10809718
- PMCID: PMC94525
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.182.11.3305-3309.2000
Evidence that SpoIVFB is a novel type of membrane metalloprotease governing intercompartmental communication during Bacillus subtilis sporulation
Abstract
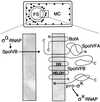
Processing of pro-sigma(K) in the mother cell compartment of sporulating Bacillus subtilis involves SpoIVFB and is governed by a signal from the forespore. SpoIVFB has an HEXXH motif characteristic of metalloproteases embedded in one of its transmembrane segments. Several conservative single amino acid changes in the HEXXH motif abolished function. However, changing the glutamic acid residue to aspartic acid, or changing the isoleucine residue that precedes the motif to proline, permitted SpoIVFB function. Only one other putative metalloprotease, site 2 protease has been shown to tolerate aspartic acid rather than glutamic acid in its HEXXH sequence. Site 2 protease and SpoIVFB share a second region of similarity with a family of putative membrane metalloproteases. A conservative change in this region of SpoIVFB abolished function. Interestingly, SpoIVFA increased the accumulation of certain mutant SpoIVFB proteins but was unnecessary for accumulation of wild-type SpoIVFB.
Figures
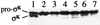

Similar articles
-
A family of membrane-embedded metalloproteases involved in regulated proteolysis of membrane-associated transcription factors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Dec 21;96(26):14765-70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.26.14765. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10611287 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane topology of the Bacillus subtilis pro-sigma(K) processing complex.J Bacteriol. 2000 Jan;182(2):278-85. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.2.278-285.2000. J Bacteriol. 2000. PMID: 10629171 Free PMC article.
-
Forespore signaling is necessary for pro-sigmaK processing during Bacillus subtilis sporulation despite the loss of SpoIVFA upon translational arrest.J Bacteriol. 2002 Oct;184(19):5393-401. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.19.5393-5401.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 12218026 Free PMC article.
-
Signal transduction in Bacillus subtilis sporulation.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Apr;3(2):203-12. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(93)90024-j. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993. PMID: 8504245 Review.
-
Differentiation and the establishment of cell type during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1991 Oct;1(3):330-5. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80296-5. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1991. PMID: 1840889 Review.
Cited by
-
Evidence for a novel protease governing regulated intramembrane proteolysis and resistance to antimicrobial peptides in Bacillus subtilis.Genes Dev. 2006 Jul 15;20(14):1911-22. doi: 10.1101/gad.1440606. Epub 2006 Jun 30. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 16816000 Free PMC article.
-
A second PDZ-containing serine protease contributes to activation of the sporulation transcription factor sigmaK in Bacillus subtilis.J Bacteriol. 2003 Oct;185(20):6051-6. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.20.6051-6056.2003. J Bacteriol. 2003. PMID: 14526016 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical and structural insights into intramembrane metalloprotease mechanisms.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Dec;1828(12):2873-85. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2013.03.032. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 24099006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Channels modestly impact compartment-specific ATP levels during Bacillus subtilis sporulation and a rise in the mother cell ATP level is not necessary for Pro-σK cleavage.Mol Microbiol. 2020 Oct;114(4):563-581. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14560. Epub 2020 Jun 29. Mol Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32515031 Free PMC article.
-
Features of Pro-σK important for cleavage by SpoIVFB, an intramembrane metalloprotease.J Bacteriol. 2013 Jun;195(12):2793-806. doi: 10.1128/JB.00229-13. Epub 2013 Apr 12. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23585539 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bron S. Plasmids. In: Harwood C R, Cutting S M, editors. Molecular biological methods for Bacillus. New York, N.Y: John Wiley & Sons; 1990. pp. 75–174.
-
- Brown M S, Goldstein J L. The SREBP pathway: regulation of cholesterol metabolism by proteolysis of a membrane-bound transcription factor. Cell. 1997;89:331–340. - PubMed
-
- Cutting S, Driks A, Schmidt R, Kunkel B, Losick R. Forespore-specific transcription of a gene in the signal transduction pathway that governs pro-ςK processing in Bacillus subtilis. Genes Dev. 1991;5:456–466. - PubMed
-
- Cutting S, Oke V, Driks A, Losick R, Lu S, Kroos L. A forespore checkpoint for mother-cell gene expression during development in Bacillus subtilis. Cell. 1990;62:239–250. - PubMed
-
- Cutting S, Roels S, Losick R. Sporulation operon spoIVF and the characterization of mutations that uncouple mother-cell from forespore gene expression in Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1991;221:1237–1256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

