Pti4 is induced by ethylene and salicylic acid, and its product is phosphorylated by the Pto kinase
- PMID: 10810149
- PMCID: PMC139926
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.12.5.771
Pti4 is induced by ethylene and salicylic acid, and its product is phosphorylated by the Pto kinase
Abstract
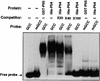
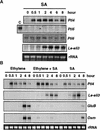
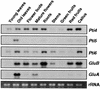
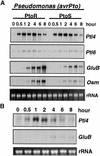
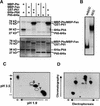
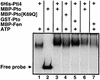
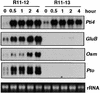
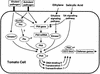
The tomato Pti4 gene encodes a transcription factor that was identified on the basis of its specific interaction with the product of the Pto disease resistance gene in a yeast two-hybrid system. We show here that the Pti4 protein specifically binds the GCC-box cis element, which is present in the promoter region of many pathogenesis-related (PR) genes. Expression of the Pti4 gene in tomato leaves was rapidly induced by ethylene and by infection with Pseudomonas syringae pv tomato, and this induction preceded expression of GCC-box-containing PR genes. Although salicylic acid also induced Pti4 gene expression, it did not induce GCC-box PR genes. Rather, salicylic acid antagonized ethylene-mediated expression of GCC-box PR genes. We demonstrate that the Pti4 protein is specifically phosphorylated by the Pto kinase and that this phosphorylation enhances binding of Pti4 to the GCC box. In addition, induced overexpression of Pto and Pti4 in tomato leaves resulted in a concomitant increase in GCC-box PR genes. Our results support a model in which phosphorylation of the Pti4 protein by the Pto kinase enhances the ability of Pti4 to activate expression of GCC-box PR genes in tomato.
Figures


References
-
- Abeles, F.B., Morgan, P.W., and Saltveit, M.E., Jr. (1992). Ethylene in Plant Biology. (San Diego, CA: Academic Press).
-
- Ausubel, F.M., Brent, R., Kingston, R.E., Moore, D.D., Smith, J.A., Seidman, J.G., and Struhl, K., eds (1987). Protocols in Molecular Biology. (New York: John Wiley).
-
- Broglie, K.E., Chet, I., Holliday, M., Cressman, R., Biddle, P., Knowlton, S., Mauvais, C.J., and Broglie, R. (1991). Transgenic plants with enhanced resistance to the fungal pathogen Rhizoctonia solani. Science 254, 1194–1197. - PubMed
-
- Buchel, A.S., Molemkamp, R., Bol, J.F., and Linthorst, H.J.M. (1996). The PR-1a promoter contains a number of elements that bind GT-1–like nuclear factors with different affinity. Plant Mol. Biol. 30, 493–504. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

