Cubilin is an albumin binding protein important for renal tubular albumin reabsorption
- PMID: 10811843
- PMCID: PMC315466
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI8862
Cubilin is an albumin binding protein important for renal tubular albumin reabsorption
Abstract
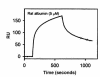
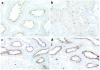
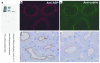
Using affinity chromatography and surface plasmon resonance analysis, we have identified cubilin, a 460-kDa receptor heavily expressed in kidney proximal tubule epithelial cells, as an albumin binding protein. Dogs with a functional defect in cubilin excrete large amounts of albumin in combination with virtually abolished proximal tubule reabsorption, showing the critical role for cubilin in the uptake of albumin by the proximal tubule. Also, by immunoblotting and immunocytochemistry we show that previously identified low-molecular-weight renal albumin binding proteins are fragments of cubilin. In addition, we find that mice lacking the endocytic receptor megalin show altered urinary excretion, and reduced tubular reabsorption, of albumin. Because cubilin has been shown to colocalize and interact with megalin, we propose a mechanism of albumin reabsorption mediated by both of these proteins. This process may prove important for understanding interstitial renal inflammation and fibrosis caused by proximal tubule uptake of an increased load of filtered albumin.
Figures




References
-
- Exaire E, Pollak VE, Pesce AJ, Ooi BS. Albumin and -globulin in the nephron of the normal rat and following the injection of aminonucleoside. Nephron. 1972;9:42–54. - PubMed
-
- Remuzzi G, Bertani T. Pathophysiology of progressive nephropathies. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:1448–1456. - PubMed
-
- Thomas ME, et al. Proteinuria induces tubular cell turnover: a potential mechanism for tubular atrophy. Kidney Int. 1999;55:890–898. - PubMed
-
- Remuzzi G. Abnormal protein traffic through the glomerular barrier induces proximal tubular cell dysfunction and causes renal injury. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 1995;4:339–342. - PubMed
-
- Schreiner GF. Renal toxicity of albumin and other lipoproteins. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 1995;4:369–373. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

