NF-kappa B inhibition causes spontaneous apoptosis in Epstein-Barr virus-transformed lymphoblastoid cells
- PMID: 10811897
- PMCID: PMC18557
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.100119497
NF-kappa B inhibition causes spontaneous apoptosis in Epstein-Barr virus-transformed lymphoblastoid cells
Abstract
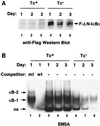
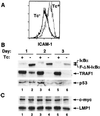
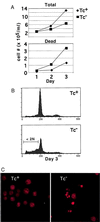
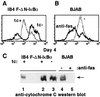
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) transforms B lymphocytes into lymphoblastoid cell lines usurping the Notch and tumor necrosis factor receptor pathways to effect transcription including NF-kappaB activation. To determine whether NF-kappaB activity is essential in the growth and survival of EBV-transformed lymphoblastoid cell lines, a nondegradable IkappaBalpha mutant was expressed under tetracycline regulation. Despite continued Bcl-2 and Bcl-x/L expression, NF-kappaB inhibition induced apoptosis as evidenced by poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase cleavage, nuclear condensation and fragmentation, and hypodiploid DNA content. Both caspase 3 and 8 activation and loss of mitochondrial membrane potential were observed in apoptotic cells. However, caspase inhibition failed to block apoptosis. These experiments indicate that NF-kappaB inhibitors may be useful in the therapy of EBV-induced cellular proliferation.
Figures



References
-
- Rickinson A B, Kieff E. In: Fields Virology. Fields B N, Knipe D M, Howley P M, editors. Philadelphia: Lippincott–Raven; 1996. pp. 2397–2446.
-
- Kieff E. In: Fields Virology. Fields B N, Knipe D M, Howley P M, editors. Philadelphia: Lippincott–Raven; 1996. pp. 2343–2396.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

