Calcium triggers an intramolecular association of the C2 domains in synaptotagmin
- PMID: 10811903
- PMCID: PMC18528
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.100127197
Calcium triggers an intramolecular association of the C2 domains in synaptotagmin
Abstract
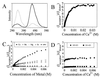
Synaptotagmin I is a critical component of the synaptic machinery that senses calcium influx and triggers synaptic vesicle fusion and neurotransmitter release. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer studies conducted on synaptotagmin demonstrate that calcium concentrations required for fusion induce a conformational change (EC(50) approximately 3 mM) that brings the two calcium-binding C2 domains in synaptotagmin closer together. Analytical ultracentrifugation studies reveal that synaptotagmin is monomeric under these conditions, indicating that this calcium-triggered association between the C2 domains is intramolecular, rather than intermolecular. These results suggest a mechanism for synaptotagmin function at the presynaptic plasma membrane that involves the self-association of C2 domains.
Figures
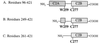

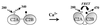
Similar articles
-
Calcium-dependent self-association of synaptotagmin I.J Neurochem. 1996 Oct;67(4):1661-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1996.67041661.x. J Neurochem. 1996. PMID: 8858951
-
The evolutionary pressure to inactivate. A subclass of synaptotagmins with an amino acid substitution that abolishes Ca2+ binding.J Biol Chem. 1997 May 30;272(22):14314-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.22.14314. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9162066
-
Localization of synaptotagmin-binding domains on syntaxin.J Neurosci. 1996 Mar 15;16(6):1975-81. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-06-01975.1996. J Neurosci. 1996. PMID: 8604041 Free PMC article.
-
The C2 domains of synaptotagmin--partners in exocytosis.Trends Biochem Sci. 2004 Mar;29(3):143-51. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2004.01.008. Trends Biochem Sci. 2004. PMID: 15003272 Review.
-
Is synaptotagmin the calcium sensor?Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2003 Jun;13(3):315-23. doi: 10.1016/s0959-4388(03)00063-1. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2003. PMID: 12850216 Review.
Cited by
-
Structure/function analysis of Ca2+ binding to the C2A domain of synaptotagmin 1.J Neurosci. 2002 Oct 1;22(19):8438-46. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-19-08438.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12351718 Free PMC article.
-
SINC, a type III secreted protein of Chlamydia psittaci, targets the inner nuclear membrane of infected cells and uninfected neighbors.Mol Biol Cell. 2015 May 15;26(10):1918-34. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-11-1530. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Mol Biol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25788290 Free PMC article.
-
A quaternary SNARE-synaptotagmin-Ca2+-phospholipid complex in neurotransmitter release.J Mol Biol. 2007 Mar 30;367(3):848-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.01.040. Epub 2007 Jan 23. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17320903 Free PMC article.
-
High metal concentrations are required for self-association of synaptotagmin II.Biophys J. 2004 Apr;86(4):2455-66. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(04)74302-7. Biophys J. 2004. PMID: 15041683 Free PMC article.
-
C2A activates a cryptic Ca(2+)-triggered membrane penetration activity within the C2B domain of synaptotagmin I.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Feb 5;99(3):1665-70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.032541099. Epub 2002 Jan 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 11805296 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rizo J, Sudhof T C. Nat Struct Biol. 1998;5:839–842. - PubMed
-
- Perin M S, Fried V A, Mignery G A, Jahn R, Sudhof T C. Nature (London) 1990;345:260–263. - PubMed
-
- Kelly R B. Curr Biol. 1995;5:257–259. - PubMed
-
- Chapman E R, Hanson P I, An S, Jahn R. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:23667–23671. - PubMed
-
- Sutton R B, Fasshauer D, Jahn R, Brunger A T. Nature (London) 1998;395:347–353. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

